Overview of lung-on-a-chip systems – The use of the alveolar-capillary barrier in human medicine
Author
Emma Thomée, PhD
Publication Date
May 26, 2020
Keywords
human medicine
disease modeling
Organ-on-a-chip
alveolar-capillary barrier
In-vitro models

Need advice for your lung-on-a-chip system?
Your microfluidic SME partner for Horizon Europe
We take care of microfluidic engineering, work on valorization and optimize the proposal with you
Introduction to lung-on-a-chip microfluidic systems
Organ-on-a-chip technology provides unique opportunities to study lung physiology and pathophysiology in vitro. The first lung-on-a-chip platforms emerged almost ten years ago, and significant progress has since been made in biological and engineering complexity.
Here, we describe one of the most sophisticated lung-on-a-chip systems in terms of biological complexity [1] that model the alveolar-capillary barrier to present current knowledge on the topic.
Structure and function of the human lung
The foremost function of the lung is to supply the body with oxygen and to get rid of the waste product of respiration – carbon dioxide.
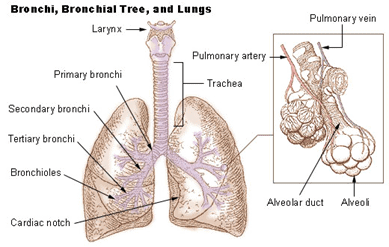
The lung has a highly branching structure. As we breathe in air, the air is driven by pressure to flow down the trachea, continuing downstream through the smaller branches until it reaches the minor structures of the lung – the alveoli.
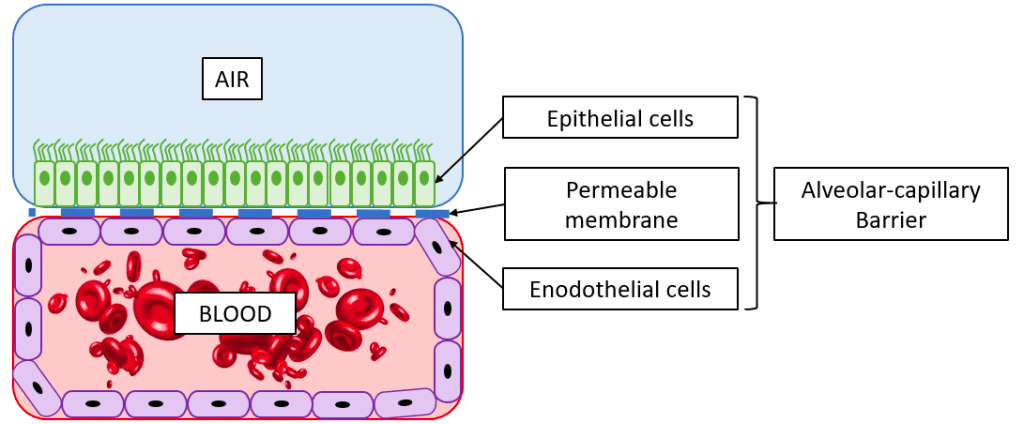
The alveoli are tiny hollow air-filled sacs surrounded by a network of capillaries. Here, in the 480 million alveoli of a human lung, the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide occurs. To enter the bloodstream, air molecules must cross the alveolar-capillary barrier, and likewise, the carbon dioxide must pass the barrier to exit the body during the exhale.
In-vitro models of the alveolar-capillary barrier
The alveolar barrier thus plays a vital role in allowing oxygen to enter the body, and failure of the alveoli can be a severe condition. Infection diseases in the alveoli, such as pulmonary edema or pneumonia, affect hundreds of millions of people globally and result in millions of deaths every year. Additionally, oral inhalation of drugs is a standard means of drug delivery, and understanding what substances can pass across the alveolar barrier is, therefore, of great importance.
As in most fields of biomedical research, animal models are commonly used to study lung pathology and to develop new treatments. Ethical issues limit the use of animal models for study, and animal lungs are substantially different from human lungs [2], limiting the translation of results. This has motivated the development of in vitro platforms for lung research. Read more about in vitro platforms for lung research here.
Organ-on-a-chip technology to model the alveolar-capillary barrier
The term “organ-on-a-chip,” as well as the technology, was developed by Donald Ingber, founder of the Wyss Institute at Harvard University. Organ-on-a-chip systems are essentially micro-engineered devices containing living cells that mimic the functions of human organs.
Donald Ingber’s team developed the seminal breathing lung-on-a-chip model that incorporated the mechanical cues of breathing in organ-on-a-chip devices. Following the first publication of this model, the team has published several studies to model different pathological conditions of respiratory diseases on-chip [3-6].
Lung-on-a-chip architecture
Read about the engineering aspects of lung-on-a-chip devices here.
Compared to the previous generation of lung-on-a-chip models, the most recent models developed by the Ingber group include the following novel features:
The use of human primary cells
Primary human lung alveolar epithelial cells and human vascular endothelial cells were seeded in the mode instead of the cancer cell line. This is important as primary cells can link the results to the donor they were acquired from – an essential step towards personalized medicine.
Furthermore, primary cells more truly replicate the diversity of human tissue compared to cell lines, which have developed homogeneous phenotypes due to passaging.
Microfluidic perfusion of whole blood
All four walls of the endothelial compartment of the chip were lined with a continuous layer of endothelial cells, forming a “vascular tube.” This enabled the perfusion of whole blood through the lumen of the vascular tube without thrombus formation, as it usually occurs if blood is perfused through a microchannel, even when coated with extracellular matrix proteins.
Discover how to do cell perfusion in a microfluidic chip for dynamic cell culture.
Disease modeling in microfluidic lung-on-a-chip systems
Mimicking pathological conditions in organ-on-a-chip models that accurately represent human physiology is of great interest for future drug development and fundamental research into respiratory diseases.
This culture model enabled experimental investigation of intravascular thrombosis under hemodynamic conditions. The disease state was induced by perfusing tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), an inflammatory stimulant, in the fluid compartment. This resulted in disease features such as platelet aggregation dose-dependent and inflammation, as also accrues in patients exposed to TNF-α.
Furthermore, this system highlighted one of the main advantages of organ-on-a-chip systems for disease modeling: the ability to study the contribution of individual tissue components of the organ compared to their cooperative responses at the organ level. This synthetic biology approach is naturally not seen in animal studies, where only system-level responses can be obtained.
Future directions of lung-on-a-chip development
Although it proved a promising technique for future lung in-vitro research, further research is needed to develop more physiologically relevant and practical systems. The biological components of lung-on-a-chip devices are still oversimplified and lack cellular components such as immune cells or neural cells.
The study presented in this review demonstrated significant improvements by using primary cells and perfusing whole blood in the system. Furthermore, the engineering aspects, such as device material, sensor integration, and compatibility with other laboratory equipment, are expected to progress in the coming years.

Review done thanks to the support of the MaMi H2020-MSCA-ITN-2017-Action “Innovative Training Networks”
Grant agreement number: 766007
Written by
Emma Thomée, PhD
Contact:
Partnership[at]microfluidic.fr

References
- Jain, A., Barrile, R., van der Meer, A., Mammoto, A., Mammoto, T., De Ceunynck, K., Aisiku, O., Otieno, M., Louden, C., Hamilton, G., Flaumenhaft, R., Ingber, D., 2018. Primary Human Lung Alveolus-on-a-chip Model of Intravascular Thrombosis for Assessment of Therapeutics. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 103, 332–340. Primary human lung alveolus‐on‐a‐chip model of intravascular thrombosis for assessment of therapeutics
- Miller, A.J., Spence, J.R., 2017. In Vitro Models to Study Human Lung Development, Disease and Homeostasis. Physiology 32, 246–260.
- Benam, Kambez H., Novak, R., Nawroth, J., Hirano-Kobayashi, M., Ferrante, T.C., Choe, Y., Prantil-Baun, R., Weaver, J.C., Bahinski, A., Parker, K.K., Ingber, D.E., 2016. Matched-Comparative Modeling of Normal and Diseased Human Airway Responses Using a Microengineered Breathing Lung Chip. Cell Syst. 3, 456-466.e4.
- Benam, Kambez H, Villenave, R., Lucchesi, C., Varone, A., Hubeau, C., Lee, H.-H., Alves, S.E., Salmon, M., Ferrante, T.C., Weaver, J.C., Bahinski, A., Hamilton, G.A., Ingber, D.E., 2016. Small airway-on-a-chip enables analysis of human lung inflammation and drug responses in vitro. Nat. Methods 13, 151–157.
- Hassell, B.A., Goyal, G., Lee, E., Sontheimer-Phelps, A., Levy, O., Chen, C.S., Ingber, D.E., 2017. Human organ chip models recapitulate orthotopic lung cancer growth, therapeutic responses, and tumor dormancy in vitro. Cell Rep. 21, 508–516.
- Huh, D., Leslie, D.C., Matthews, B.D., Fraser, J.P., Jurek, S., Hamilton, G.A., Thorneloe, K.S., McAlexander, M.A., Ingber, D.E., 2012.
A human disease model of drug toxicity-induced pulmonary edema in a lung-on-a-chip microdevice. Sci. Transl. Med. 4.
Check the other Reviews
FAQ - Overview of lung-on-a-chip systems – The use of the alveolar-capillary barrier in human medicine
What is the lung-on-chip technology?
Lung-on-chip devices are microfluidic systems that mimic the alveolar-capillary interface, the primary site of gas exchange in the human lung. These chips culture lung epithelial cells and endothelial cells on opposite sides of a porous membrane under fluidic conditions to simulate mechanical breathing movements and provide a physiological microenvironment, thereby modeling lung mechanisms, pathology, and drug response.
How can the MIC contribute to the development of the lung-on-chip?
MIC has a full organ-on-chip design capability, such as:
Gas exchange (O2/CO2) and selective transfer membrane engineering.
Flow co-culture and shear stress management mechanisms.
Onboarding of functional readouts such as TEER sensors, metabolic sensors, etc.,
Multi-physics modeling of the optimization of flow patterns and mechanical stimulation.
How can the MIC combine detection and monitoring in lung-on-chip systems?
MIC designs sensing solutions:
Optical systems: Cellular response and barrier integrity fluorescence imaging, which is a quantitative method.
Physical sensors: Inbuilt temperature, pressure, O2, and pH,
Electrical measurements: TEER assessing real-time barrier function using Impedance.
What MIC instruments are available to be used in lung-on-chip experiments?
MIC is a designer of full fluidic systems:
Exact pressure/flow control and multi-channel structures and minimal pulsation,
Breathing simulation programmable pumps and pneumatic breathing simulation valves,
Real-time controllable embedded electronics and PC/Cloud enabled,
Upstream processing sample conditioning modules.
Does MIC have the capability of coming up with AI-based solutions on lung-on-chip platforms?
Indeed, MIC applies AI throughout the development chain:
Automated cell segmentation, tracking and morphological analysis Computer vision,
Real-time feedback of sensor controls on adaptive control of flow and mechanical stimulation,
Design optimization Latent CFD simulations with machine learning channel geometry,
Identification of pathological cellular responses performed by the rare event detection.
What is the response to regulatory needs of applications of lung-on-chip?
MIC incorporates the regulatory thinking in the development:
Material biocompatibility Cytotoxicity testing, extractables/leachables analysis to comply with medical devices,
Design for regulation (DfReg): Interpretation of the ISO 13485 and MDR on organ-on-chip systems,
Validation procedures: Multi-parameter robustness test and reliability planning.
What MIC software capabilities does it have on lung-on-chip systems?
MIC builds up entire software stacks:
Protocol programming and experiment control user interfaces,
Standardization and cloud integration data management infrastructure,
Predictive control and optimization Digital twin models,
Pharmaceutical workflow API integration with LIMS systems.
Is MIC able to support academic research and commercial products development?
Absolutely. MIC interfaces research-to-market:
Academic cooperation Custom chip design, special fabrication and research instrumentation,
Development of industries: Design of Manufacturing (DfM), production methods which are scalable and architecture of systems,
Consortium management: Academic-industrial project management on EU-funded projects.
What are some of the differences in the organ-on-chip technology of MIC?
MIC offers another feature of end-to-end integration of systems as opposed to standalone components:
Full simulation of pipeline physics – chip creation – instrumentation,
Striking a balance between the cutting-edge capabilities (green highlights) and strategic growth areas (limited blue additions),
The governmental awareness during the initial design up to validation,
Biological (organ-on-chip), diagnostic, and new market experience (thermal management).
This is systems-level experience that puts MIC in a position to be a complete developer of lung-on-chip technology through concept to validated platform.

