Neutrophil chemotaxis pack
Follow neutrophil chemotaxis in real time ideal physiological conditions
High quality image gathering
Follow your neutrophils in real time
Keep the ideal temperature conditions
Culture cells on top of the microscope stage
Use the chip of your preference
Setup can be used with any chip design

Need a microfluidic SME partner for your Horizon Europe project?
Neutrophil chemotaxis pack
Neutrophil chemotaxis is one of the first lines of defense
Neutrophils are usually the first immune cells, not ordinarily present in the tissue, recruited to an inflammation or injury site [1]. They typically reside in the bone marrow and are attracted to these sites by cytokines released by infecting agents or local immune cells, such as macrophages [2].
Once circulating in the blood, neutrophils detect the location of the injury by the surrounding activated endothelial cells, which causes them to slow down and migrate into the tissue [1].
Gradients are responsible for neutrophil chemotaxis
Chemotaxis is an essential physiological process involved in embryonic development, wound healing, immune response, and even cancer progression [3], making its understanding crucial for advancements in drug development.
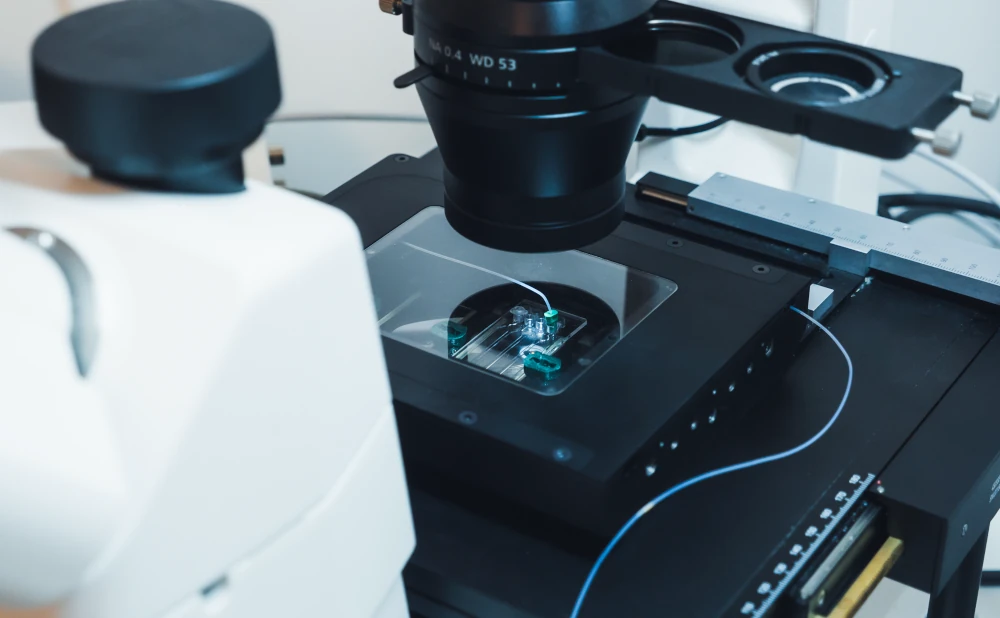

Maintain your neutrophils under ideal conditions during experiments
Our Stage Top Incubator was designed to keep the physiological temperature during long-term dynamic experiments on top of the microscope stage. You can couple it with gradient-forming chips and perform experiments under flow, mimicking the chemotaxis of neutrophils in the blood vessels.
References
1. Grigolato, F, Egholm, C, Impellizzieri, D, Arosio, P, Boyman, O. Establishment of a scalable microfluidic assay for characterization of population-based neutrophil chemotaxis. Allergy. 2020; 75: 1382– 1393. https://doi.org/10.1111/all.14195
2. Wu, X., Newbold, M.A., and Haynes, C.H. Recapitulation of in vivo-like neutrophil transendothelial migration using a microfluidic platform. Analyst, 2015,140, 5055-5064. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5AN00967G
3. Ren, J., Wang, N., Guo, P., Fan, Y., Lin, F., and Wu, J. Recent advances in microfluidics-based cell migration research. (Critical Review) Lab Chip, 2022, 22, 3361-3376. DOI: 10.1039/D2LC00397J
Neutrophil chemotaxis pack setup
Neutrophil chemotaxis can be quickly followed on top of the microscope stage with the suggested setup, which comprises a flow controller, flow sensors, and the stage top incubator. The chip can be adapted to your specific application. We can suggest commercially available options, such as the Fluidic 834 from ChipShop, but in-house developed devices can be equally used.
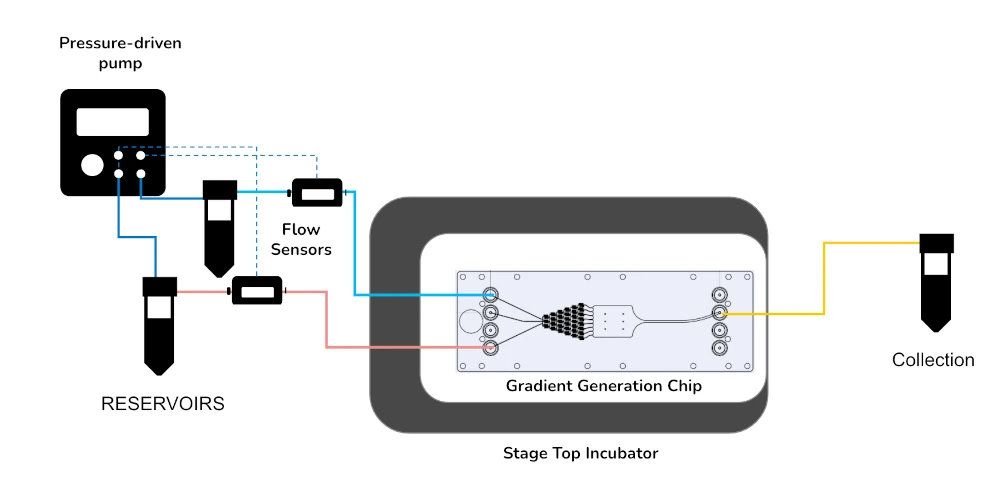
The neutrophil chemotaxis pack includes:
Flow sensor (Galileo, MIC)
Stage top incubator (in development)
Software (Galileo user interface)
Flow controller
2 x 15 mL falcon reservoirs
Chip from microfluidic ChipShop (suggestion: Fluidic 834)
All necessary accessories: tubing, connectors, filters, etc.
Applications of neutrophil chemotaxis
Performing chemotaxis experiments in microchannels have marked advantages. It is possible to study the heterogeneity of populations by analyzing them at the single-cell level [1]. It is also possible to better replicate the microenvironment of neutrophils during migration from the bone marrow to the injury site by applying liquid flow.
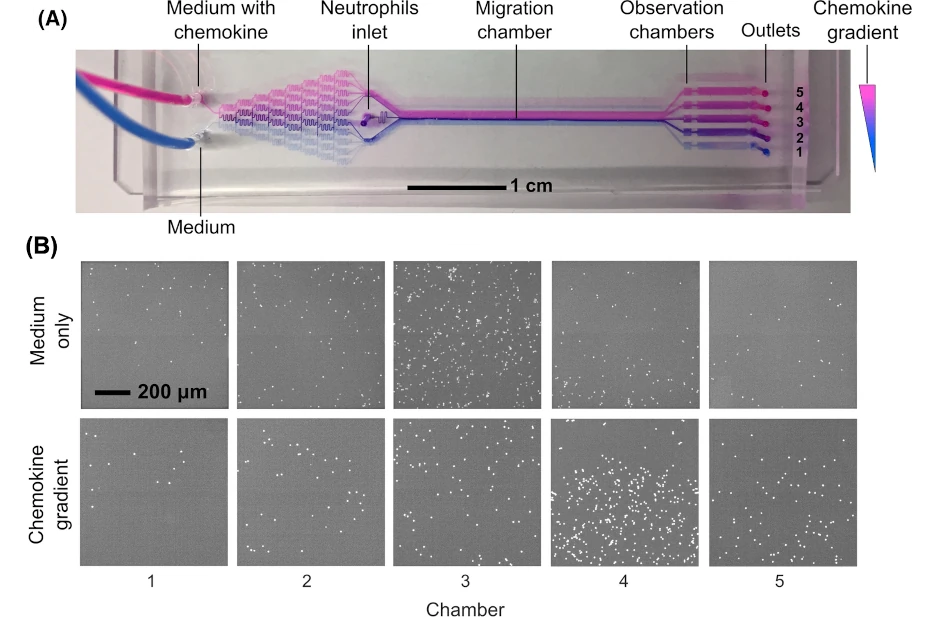
Grigolate et al. [2] have developed a platform for studying neutrophil chemotaxis due to chemokine gradients that profit precisely from that.
Their in-house developed chip creates gradients collected in different chambers at the outlet. Neutrophils are introduced after gradient formation, and the flow is adjusted to allow for an adequate residence time of neutrophils for detectable chemotactic motion. Their results showed a clear preference for the neutrophils for Chamber 4 when chemokines were used, indicating the best distribution of the chemoattractant [2], as shown below.
References
1. Ren, J., Wang, N., Guo, P., Fan, Y., Lin, F., and Wu, J. Recent advances in microfluidics-based cell migration research. (Critical Review) Lab Chip, 2022, 22, 3361-3376. DOI: 10.1039/D2LC00397J
2. Grigolato, F, Egholm, C, Impellizzieri, D, Arosio, P, Boyman, O. Establishment of a scalable microfluidic assay for characterization of population-based neutrophil chemotaxis. Allergy. 2020; 75: 1382– 1393. https://doi.org/10.1111/all.14195
Customize your pack
Our Products and Packs are fully customizable to fit your needs perfectly. Our specialists and researchers will help you choose the best instruments and accessories and accompany you during the setup of the microfluidic platform.
Contact our experts to answer any questions about this stage top incubator for microfluidics pack and how it can match your specifications!
Frequently asked questions
Can I order a pack?
Since Packs are products that are still being developed, we have a few eligibility criteria to maximize their success rate. A discussion with our experts is needed to determine your specific needs to offer you a personalized response.
Can a pack be customized based on my specific application?
Yes! Our experts will establish which instruments are best suited for your application, such as the type of flow sensor or the number of flow controller channels you need to perform your experiment. Contact us using the “talk to our experts” green button above.
Can I buy individual instruments?
Our instruments are in beta testing phase and can be tested as a pack or individually, so get in contact with our team to know how our beta testing program works.



Funding and Support
Products & Associated Accessories
FAQ - Neutrophil chemotaxis pack
What is its solution to the problem of classical chemotaxis assays?
Classical assays (Transwell-type approaches) may be ideal in screening, but are typically incapable of (i) gradient stability cell tracking, (ii) operating in real-time, and (iii) recreating flow-based features of vascular-like environments. Gradients Microfluidic gradient-forming chips have been used to create more controlled, observable gradients and to use lower volumes of reagents than in bulk methods.
So, what’s in the pack?
The “core” pack is built around:
-A flow controller
-Flow meters (especially the Galileo flow meter of MIC)
-A stage-top incubator (designed to provide physiological temperature in experiments of some duration on the microscope)
-The arrangement is coherently pilotable via software (Galileo user interface).
-Two 15 mL Falcon reservoirs
-All the working accessories (tubing, connectors, filters, etc.)
-Microfluidic chip itself is flexible: it can be one of the available chips (MIC cites an example of Fluidic 834 by ChipShop) or a homemade solution.
What is so important about the stage-top incubator?
Due to the fact that neutrophils are unforgiving when the conditions are off track. When you track it over time on a long scale, temperature stability becomes one of those boring details that will silently give your data a sharp or shaky appearance. The stage-top incubator will maintain experiments at physiological temperature, and you can image continuously at the microscope stage without moving devices in and out of incubators, hoping nothing will change.
Is it possible to use my own chip design or do I have to stick to a particular microfluidic device?
You’re not locked in. The system is configured to fit just about any chip design, which works as long as the fluidic interfacing is sensible. Assuming you already have a gradient generator design that has been tested in your lab, this pack is intended to add the control/measurement layer (flow control, sensing, temperature stability, software) and the so-called clean integration that avoids leaving your design as a spaghetti of adapters.
What type of gradients are we discussing (why would this be important)?
The underlying concept of neutrophil chemotaxis is the directional response to the gradient of chemokines/cytokines released by pathogens or local immune cells (and, more generally, to physiological processes such as wound healing and immune recruitment). Geometric and flow-ratio engineering in microfluidics to create a stable, reproducible gradient; gradient formation is generally engineered. It is also why microfluidic chemotaxis is widely used in the study of neutrophil migration: it can be visualized, and gradients can be controlled in real time.
What are the common measures that people derive from the live neutrophil tracing?
The foundations of most teams include single-cell trajectories, velocity, directionality, chemotactic index, persistence, followed by a more ambitious step: heterogeneity in the population, responder versus non-responder fractions, or phenotype changes in response to drug treatment. Microchannels simplify quantification at single-cell resolution by avoiding averaging across multiple endpoints.
What about the customization (channels, sensors, configuration)?
The point of customization is important. MIC can customize:
-The type of flow sensor
-Channels of flow controllers
-The interfacing fluidic accessories.
-The chip option (commercial recommendation or your own)
Practically, this is what will make the difference between being able to make one sort of pretty demo and having a solid experimental program that can last an actual day.
Is it possible to purchase single instruments rather than a pack?
Potentially yes. According to MIC, their instruments are at the beta stage of testing and may be tested as a pack or individually, depending on the structure of their beta testing program. When you already have part of the hardware stack and only require (say) sensing, software, and stage-top incubation, this is the type of conversation you want to have at the beginning, before you reinvent your entire system based on false premises.
What is the relation of this to Horizon Europe / EU collaborative projects?
Many Horizon Europe health and biotech themes have chemotaxis, inflammation, infection, and immune-on-chip themes central to them. A microfluidics-oriented SME partner can leave much of the risk on the engineering side: design of setups, prototyping, chip plan, integration, reproducibility, and the always tedious but deadly-looking bits of fluidic interfacing and validation. And, more realistically, when a consortium has a partner capable of building and testing prototypes (not writing about them), proposals will seem more plausible to evaluators, particularly in packages of work involving technology.

