Fluids Serpentine Micromixer Platform
Multi-fluid mixing straight out of the box using micromixer pack
Microfluidic setup for passive mixing
Unbox, set up and start your experiments right away
Planar serpentine micromixer
No need for active mixing device as magnetic stir bar
Rapid effective mixing
Good homogeneity at the channel outlet

Need a microfluidic SME partner for your Horizon Europe project?
Serpentine channel drawing figure by Clark et al. (2018)
Microfluidic flow micromixing
Mixing up to four fluids in a microfluidic channel has never been easier using the microfluidic serpentine micromixer Pack for many applications like immunoassays, mixing PCR solutions, or chemical synthesis!
Based on a flow controller and a planar meander mixing chip, this all-in-one solution contains all the required pieces for researchers to set up their mixing system with a high flow rate and mixing efficiency. Our microfluidic expert will accompany you during all the steps needed to setup and perform your micromixing experiment.
A standard multi-fluid mixing serpentine planar micromixer Pack contains pumping channels to push at least two fluids to mix through the serpentine micromixer chip, allowing the rapid creation of a homogenous fluid at the outlet of the chip by inducing a speed gradient in the channel.
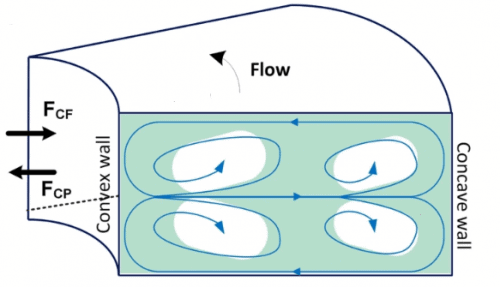
The fluid circulating in the serpentine-shaped channel is faster near the outer walls of the microchannel than near the inside walls of the channels, thus inducing the creation of vortices, which allow the mixing of the different fluids inside the microchannel.
The efficiency of the mixing will be directly linked to the fluid’s properties and the flow rate inside the channel. The flow controller precisely tunes flow rates, which can be measured by flow rate sensors.
Serpentine micromixer pack setup
An all-in-one pack guaranties a good compatibility between the different microfluidic instruments and accessories, allows the start the experiment right out the box, is piloted by a single software and can be used for other different applications. These highlights pushed us to assemble this Pack for beginner and expert users.
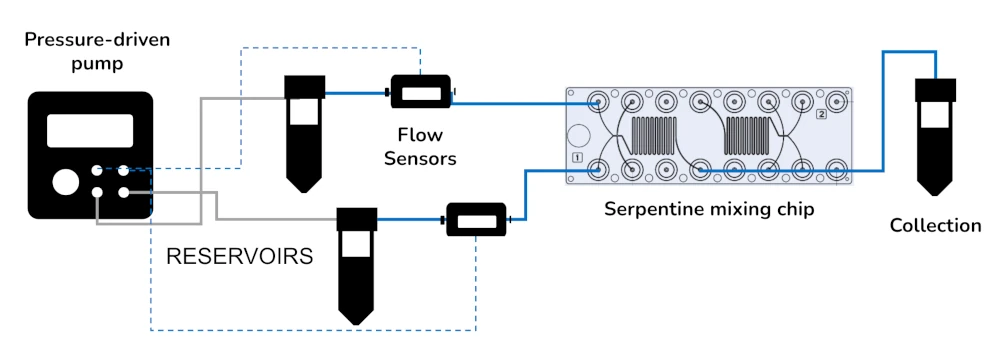
A typical pack contains:
Flow sensor (Galileo, MIC)
Software (Galileo user interface)
Flow controller
Falcon reservoirs
Microfluidic chip from microfluidic ChipShop
All necessary accessories: tubing, connectors, filters, etc…
Why use microfluidics for fluid mixing
Microfluidics uses tiny volumes of sample which is very efficient to decrease the amount of expensive sample needed for experiment.
Moreover, at the microfluidic scale fluid properties can be precisely tuned and very fast kinetics is possible which is important for crystallization and precipitation processes for synthesis of polymeric nanoparticles for example.
Microfluidics also enable to precisely control reactions in the micromixer by adding specific reagents at specific moments during the experiment.
Micromixers allow the reaction to isothermal thanks to the increased heat transfer in microreactors.
Since planar serpentine micromixers are miniaturized, this mixing part can be implemented in a more complete experiment platform to perform complicated and multifunctional integrated process.
To summarize, micromixers chips allow more flexible, precise and efficient mixing between two fluids.
References
Nivedita, Nivedita, Phillip Ligrani, and Ian Papautsky. “Dean flow dynamics in low-aspect ratio spiral microchannels.” Scientific Reports 7.1 (2017): 44072.
Microfluidics serpentine micromixer principle
Mixing is a crucial step in a lot of different microfluidic applications [1]. The planar serpentine micromixer (PSM) chip creates mixing because of a liquid speed difference in the turns between the inner and the outer wall improving the mixing [2].
The mixing by diffusion in a straight microchannel is too slow to be useful in microfluidics setups as a typical flow in microfluidics setups is laminar and consequently without the turbulence that induces mixing.
This design creates a transversal advection for intermixing different components in the microchannel [3-4]. Indeed, the PSM chips are an effective and straightforward way to mix without using any external power source and thus can be modeled more efficiently than more complex techniques [5].
Micromixing using a serpentine micromixer can be helpful and an improvement for various applications like combinatorial or organic chemistry, handling hazardous substances, PCR, screening and many more [6-9].
References
Lee, Chia-Yen, et al. “Microfluidic mixing: a review.” International journal of molecular sciences 12.5 (2011): 3263-3287.
Nivedita, Nivedita, Phillip Ligrani, and Ian Papautsky. “Dean flow dynamics in low-aspect ratio spiral microchannels.” Scientific Reports 7.1 (2017): 44072.
Nguyen, Nam-Trung. Micromixers: fundamentals, design and fabrication. Micro & nano technologies. William Andrew (2011).
Scherr, Thomas, et al. “A planar microfluidic mixer based on logarithmic spirals.” Journal of Micromechanics and Microengineering 22.5 (2012): 055019.
Kee, Suet Ping, and Asterios Gavriilidis. “Design and characterisation of the staggered herringbone mixer.” Chemical Engineering Journal 142.1 (2008): 109-121.
Wilms, Daniel, Johannes Klos, and Holger Frey. “Microstructured Reactors for Polymer Synthesis: A Renaissance of Continuous Flow Processes for Tailor-Made Macromolecules?” Macromolecular Chemistry and Physics 209.4 (2008): 343-56. Print.
Zhang, Chunsun et al. “Micropumps, microvalves, and micromixers within PCR microfluidic chips: Advances and trends.” Biotechnology advances vol. 25,5 (2007): 483-514.
Dittrich, Petra S et al. “Micro total analysis systems. Latest advancements and trends.” Analytical chemistry vol. 78,12 (2006): 3887-908.
Dittrich, Petra S, and Andreas Manz. “Lab-on-a-chip: microfluidics in drug discovery.” Nature reviews. Drug discovery vol. 5,3 (2006): 210-8.
Customize your pack
The planar serpentine micromixer chip provided by Microfluidics ChipShop is available in Polycarbonate (PC) or Cyclo Olefin Copolymer (COP) materials, channel depth: 100 µm; channel width inlet: 100-200 µm; channel width mixer: 200 µm; channel width outlet: 200 µm. The efficiency of the mixing depends on the Reynolds and the Peclet number. For advice on a specific application, contact one of our experts!
Up to 4 fluids can be mixed using the microfluidic serpentine micromixer pack with the same microfluidic chip and four flow controller active channels. Consequently, additional flow rate sensors can also be provided.
Bubble can be a problem when mixing; bubble remover that can tackle this issue can be provided if this issue is critical for the experiment.
Substance mixing can also be achieved with other strategies like herringbone micromixers.
Contact our experts for any questions about this fluid mixing pack and how it can match your specific application.
Frequently asked questions
How can we help your experiment
This pack is in beta testing phase. So, although the instruments are not fully industrialized, we can provide extensive support as part of our beta testing program. Get in touch to see if you are eligible.
Can a pack be customized?
Yes! Our experts will establish which instruments are best suited for your application, such as the type of flow sensor or the number of flow controller channels you need to perform your experiment. Contact us using the “talk to our experts” green button above.
Can I buy individual instruments?
Our instruments are in beta testing phase and can be tested as a pack or individually, so get in contact with our team to know how our beta testing program works.
Products & Associated Accessories
FAQ - Serpentine micromixer pack
What is the Multi-Fluid Serpentine Micromixer Pack?
It is a microfluidic one-stop solution, which is capable of combining up to four fluids in a two-dimensional serpentine-patterned microchannel. The pack contains all the instruments and accessories required to assemble a passive mixing experiment right out of the box with professional assistance on each step.
The operation of a serpentine micromixer: how does this work?
Passive fluid dynamics instead of any external power source is used to achieve mixing. Due to the circulation of fluids in the serpentine (meander-shaped) channel, the velocity of the flow varies between the inner and outer walls of each of the curves. Such a velocity gradient creates transversal vortices – rotating flow structures, which mix the streams of fluid gradually. The higher the flow rate and the more vivid the physical characteristics of the fluid, the better the mix.
The advantages of microfluidics over traditional methods of fluid mixing?
Microfluidic mixing presents a number of practicable benefits:
-Sample efficiency: Small volumes of fluid are used in experiments, which saves the use of expensive reagents.
-High-dimensional control: Flow rates are controllable with fine precision, which allows reaction kinetics to be run in a rapid and repeatable fashion – essential in reactions such as nanoparticle synthesis or crystallization.
-Isothermal reactions: In microchannels the ratio of surface-volume is huge; this allows the reaction to be maintained at a constant temperature.
-Reagent timing: It is possible to add specific reagents at a specific time point during an experiment.
-Integration: The miniaturized format can be built in planar into larger multifunctional platforms-on-a-chip.
What does a typical pack entail?
A typical pack contains:
-A flow controller to accurately control the flow of fluids.
-A chip planar serpentine chip of a micromixer (Microfluidic Chipshop).
-Flow rate gauges (Galileo, MIC)
-Galileo end user software.
-Falcon fluid storage reservoirs.
-All accessories: filters, connectors and tubing.
Every element is chosen to be compatible with each other and the whole system is controlled through one software interface.
Which chip materials and chip sizes do we have?
Serpentine micromixer chip comes in two thermoplastics:
-Polycarbonate (PC)
-Cyclo Olefin Copolymer (COP)
Normal dimensions of the channels are:
-Channel depth: 100 um
-Channel width at inlet: 100-200 um
-Mixer and outlet channel width: 200 um.
The efficiency in mixing is proportional to the Reynolds number (inertial and viscous forces) and Peclet number (convective and diffusive transport). Call the MIC team and get specific advice on your fluid system.
What is the maximum number of fluids to be mixed?
A single chip can be connected to four flow channels in order to mix up to four fluids. More flow rate sensors may be supplied to measure each stream of inlet separately.
What are the primary areas of use of this pack?
Serpentine micromixer is applicable to wide variety of research and applied situations including:
-Immunoassays and preparation of biological reagents.
-PCR solution mixing
-Combinatorial chemistry and Chemical synthesis.
-Hazardous organic chemistry (taking advantage of small and contained volumes)
-Synthesis of nanoparticles made of polymers.
-Drug screening and discovery.
Can the pack be used by microfluidics novice users?
Yes. The pack is clearly made to target both the amateur and expert users. The all-in-one design allows eliminating the compatibility problems with instruments, and microfluidic specialists at MIC would assist during setup and experimentation. The single software interface (Galileo UI) also eases the user.
Is the pack application-specific?
Yes. MIC specialists will analyze your application needs and decide on the best possible configuration that would include:
-The nature and amount of flow sensors.
-The quantity of flow controller channels
-The existence of other accessories (like bubble removers) required.
-The fact that bubbles can develop during mixing experiments may be a convenient aspect; they can be removed by bubble remover modules in case it is vital to your process.
What are some other mixing plans in case the serpentine design does not work?
Yes. MIC has also a herringbone micromixer pack that utilizes a different channel geometry to obtain mixing. The decision between serpentine and herringbone design is based on your flow regime, fluid and integration needs. Compare and recommend to the MIC team.
Is the pack available at present?
The pack will be on a beta testing stage. Although the tools are not yet industrialized, MIC does offer much assistance to the beta testers. The team may be approached by interested users to find out the eligibility and discuss the terms of the beta program.
Is it possible to buy instruments separately as opposed to buying them in a pack?
Yes, individual instruments can be tested not only in the complete pack format. Contact the MIC team to know the application of the beta testing program to standalone instruments.

