Thermoplastic Molding Microfluidics Setup
With only a few changes in your current microfabrication process
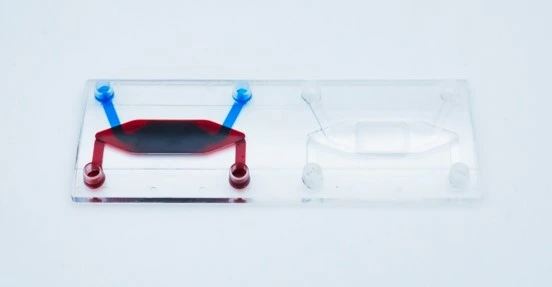
COC, PMMA, PS, choose what best fits your needs
Fabricate thermoplastic chips in only 1 hour
Why switch to thermoplastic molding?
PDMS has been the working horse of microfluidics since its beginning. But as the technology leaves its infancy and starts to mature, the limitations of PDMS start to outweigh its perceived benefits, such as its easy and quick microfabrication process.
Limited chemical compatibility, high gas permeability, and low throughput are reasons why researchers started looking for replacement materials, such as thermoplastics.
However, thermoplastic molding for microfluidic chip fabrication can sound daunting as a process, as it evokes extensive industrial facilities and complex machinery.

With that in mind, we challenged our capable team of engineers and researchers to come up with a way to adapt the current PDMS microfabrication process and turn it into a thermoplastic molding setup for microfluidic chip fabrication. And they were up to the challenge!
Let’s have a look at what they came up with:
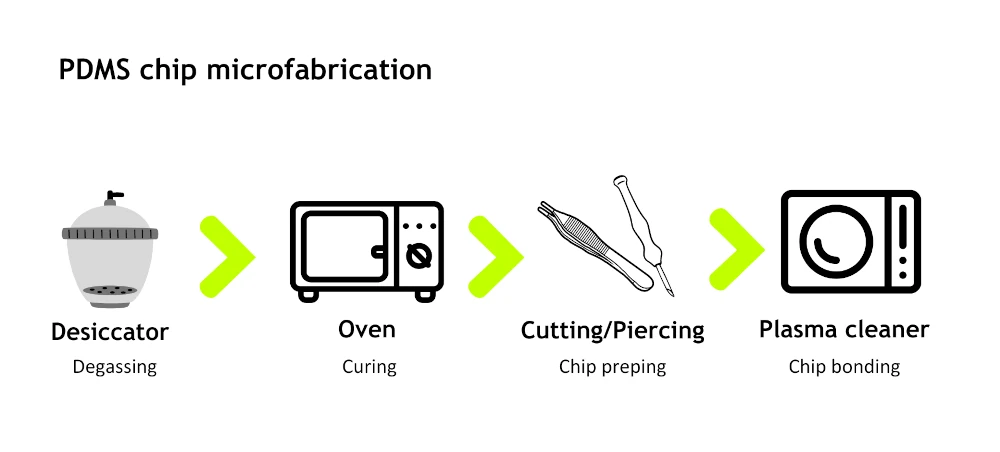
The PDMS microfabrication process starts with mixing PDMS with a curing agent and degassing inside a desiccator. Then, the elastomer is poured over the mold and cured in a conventional oven. Once ready, the chips are demolded and cut, and inlets are pierced with biopsy punchers. Lastly, the PDMS is bound to a glass slide after treatment in a plasma cleaner.
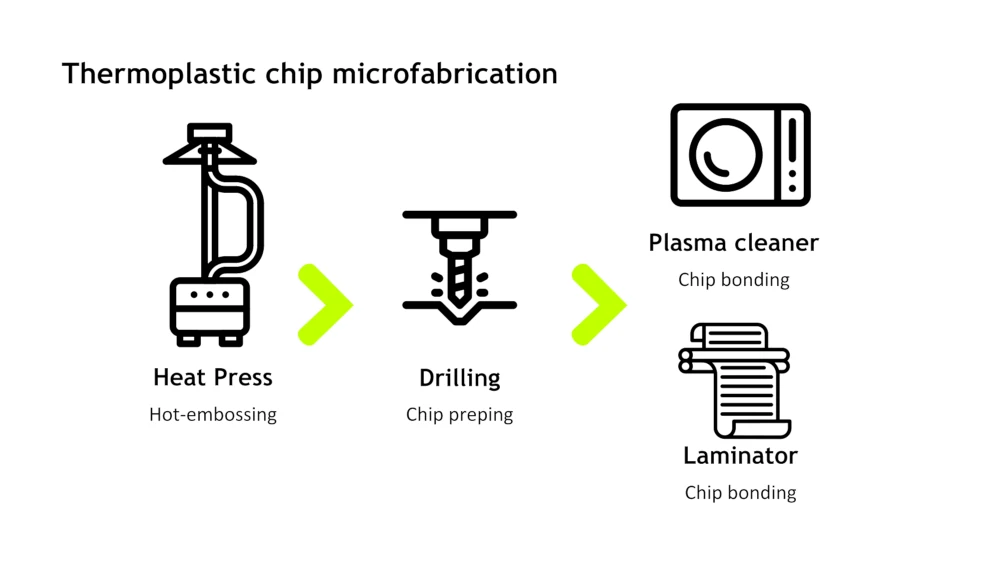
In our thermoplastic molding microfluidic setup, you substitute the first time-consuming part of the process with a much quicker hot-embossing process. Then, the chip prepping can be done with drilling tools. You will use the same plasma cleaner you already have to close your chip, with an additional step with a laminator.
So, you only have to add our recommended heat press and laminator to your workflow and follow our instructions to be able to turn our PDMS microfabrication into a thermoplastic molding setup.
Your PDMS microfabrication process is different, and you don’t have all the listed equipment? Don’t worry; we’ve got you covered! We can provide you with all the necessary pieces and consumables; just drop us a line!
Technical specifications
The thermoplastic molding microfluidic setup comprises:
Heat press with Double Heating Plate:
- Dimensions:420*550*680mm.
- Max temperature: 300℃.
- Pressure range: 0-25 tons.
Laminator
- Dimensions: 270*545*130 mm (L x w x h)
- Max. laminated width: 335 mm
- Max. laminated thickness: 35 mm
- Max temperature: 140 °C.
Options: Drilling machine
Consumables: Thermoplastic sheets of choice.
Compatibility and Applications
The thermoplastic molding setup can be used with:
- PMMA
- COC
- PS
- Virtually any other thermoplastic
Applications are usually material-dependent, but in general terms, microfluidics chips produced with thermoplastic molding can be employed in:
- Lab-on-a-chip applications, such as nanomaterial synthesis
- Cell culture experiments, such as gut-on-a-chip
- Applications requiring specific-chip design and chemical inertia
Does the process also involve mold fabrication?
Currently, the thermoplastic molding microfluidic setup focuses on the chip fabrication and bonding from a pre-existing mold. However, we do have expertise to advise you in how to make your own molds.
What is the resolution of the thermoplastic microfluidic devices?
It depends on the chosen material, but for the PMMA devices done with this thermoplastic molding setup, for example, resolutions as low as 15 µm (channel width) for an aspect ratio of 2:1 can be achieved.
What maximum pressure can the devices withstand?
Based on internal testing, up to 3.5 bar.
What material can I use to close the chip?
The chip can be closed with a thermoplastic slide, a microscope glass slide or a microscopy-compatible polymer slide.
Is this process compatible with microscopy/reversed microscopy?
It depends on the properties of your thermoplastic of choice. PMMA, for example, is optically transparent and well-adapted to microscopy.
Funding and Support
The BIOPROS and MICRO4NANO projects results helped develop this instrument pack, with funding from the European Union’s Horizon research and innovation program under HORIZON-CL4-2021-DIGITAL-EMERGING-01-27, grant agreement no. 101070120 and the European Union under H2020-MSCA-RISE-2020, grant agreement No. 101007804.
Special thanks to Micaela Fernandes and Widad Mesbahi, who largely contributed to the development of this pack.


