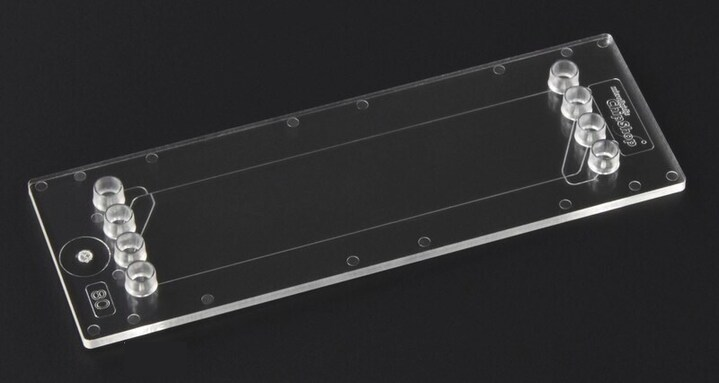
COC Polymer Molding Microfluidics Setup
From PDMS to low-impurity high-performance COC polymer
Fast process
Fabricate plastic COC chips in only 1 hour
No clean room required
The entire microfabrication process takes place outside of a clean room
Adaptable to your needs
Easily shaped into any form or dimension

Need a microfluidic SME partner for your Horizon Europe project?
COC polymer molding microfluidics setup
From manufacturing PDMS chips …
The most common material for microfluidic device fabrication is PDMS.
PDMS chip fabrication takes place outside a clean room. It starts by mixing PDMS with a curing agent and degassing it in a desiccator. Then, it is poured onto a mold and cured in a standard oven. Once cured, the chips are demolded, precisely cut, and have inlet holes created using biopsy punchers. Finally, plasma cleaner treatment firmly sticks the PDMS to a glass slide.
Yet, PDMS’s limited chemical compatibility, high gas permeability, and low throughput hinder its use in many critical applications. That is why researchers are shifting towards alternative materials such as cyclic olefin copolymer (COC) plastic.
… To COC polymer molding!
Plastic COC provides many advantages for chip microfabrication. It is noted to be a high purity product with excellent optical properties. It is biocompatible and exhibits high chemical resistance. Its moisture insensitivity and gaz permeability can turn out to be real assets in many applications. Furthermore, its ease of fabrication and modification offers a great versatility of design.
Microfabrication of COC polymer follows the same steps as for the thermoplastic chip microfabrication, and both can be performed outside of a clean room. Our setup is also compatible with the homopolymer COP.
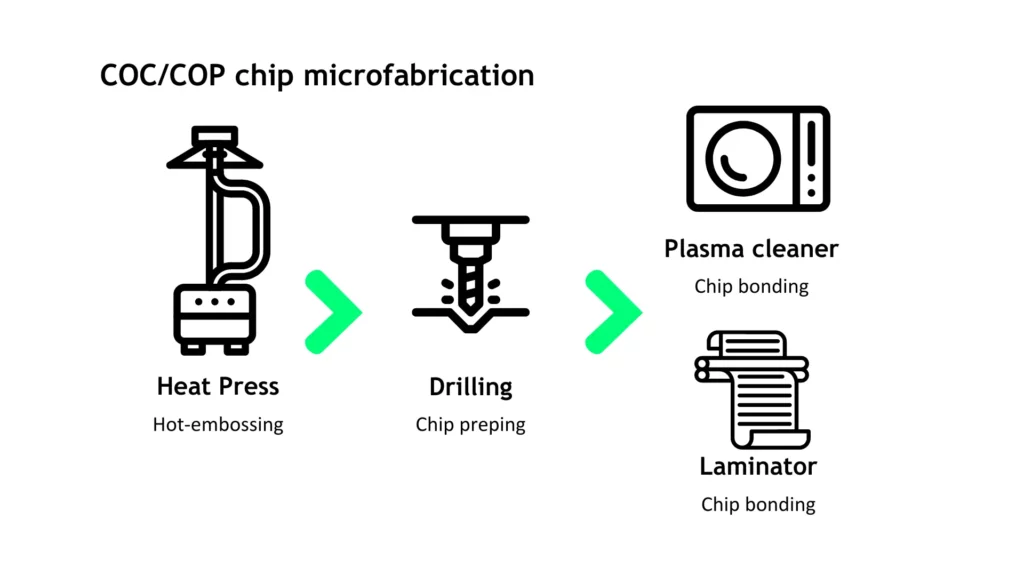
By following our instructions and adding the recommended heat press and laminator, you can smoothly shift from PDMS microfabrication to a COC polymer molding setup.
Your PDMS microfabrication process is different, and you don’t have all the listed equipment? Don’t worry; we’ve got you covered! We can provide you with all the necessary pieces and consumables; just drop us a line!
We recently published a review about the diverse materials and innovative fabrication and molding techniques used in microfluidic chip design.
Compatibility and applications
The COC polymer molding setup can also be used with:

PMMA device station
From mold development to high-resolution PMMA chip fabrication
✓ Fast process
✓ Multiple applications
✓ Simple and innovative setup
PMMA

Polystyrene (PS) molding microfluidics setup
From PDMS to highly versatile and transparent Polystyrene PS
✓ Fast process
✓ No need for a clean room
✓ High versatility
Polystyrene

Polycarbonate (PC) molding microfluidics setup
From PDMS to highly versatile and performant Polycarbonate PC
✓ Fast process
✓ No need for a clean room
✓ High impact strength
Polycarbonate
And many more!
Microfluidic chips produced with COC polymer molding can be employed in:
Microfluidics nanomaterial synthesis pack
Microfluidics for production of nanomaterials using sheath flow focusing
✓ Efficient synthesis. ofnanomaterials
✓ Easy microfluidic system implementation
✓ Biomedical applications
Lab-on-a-chip applications (e.g. nanomaterial synthesis)
Gut-on-a-chip pack
Intestinal cells coculture under flow, mimicking the gut physiology
✓ All microfluidic pieces included, quick and easy assembly
✓ Dynamic culture conditions
✓ Advanced in viro/ex vivo
Gut-on-chip
Applications requiring specific-chip design and chemical inertia
And many more!
Technical specifications
The COC polymer molding microfluidic setup comprises:
Heat press with double heating plate
| Components | Specifications |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 420*550*680mm |
| Max temperature | 300 °C |
| Pressure range | 0-25 tons |
Laminator
| Components | Specifications |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 270*545*130 mm (L x w x h) |
| Max laminated width | 335 mm |
| Max laminated thickness | 35 mm |
| Max temperature | 140 °C |
Options: Drilling machine
Consumables: Plastic COC sheets
Frequently asked questions
Does the process also involve mold fabrication?
Currently, the COC polymer molding microfluidic setup focuses on the chip fabrication and bonding from a pre-existing mold. However, we do have expertise to advise you in how to make your own molds.
What is the resolution of the COC microfluidic devices?
Resolutions as low as 15 µm (channel width) for an aspect ratio of 2:1 can be achieved.
What maximum pressure can the devices withstand?
Based on internal testing, up to 3.5 bar.
What material can I use to close the chip?
The chip can be closed with a thermoplastic slide, a microscope glass slide or a microscopy-compatible polymer slide.
Is this process compatible with microscopy/reversed microscopy?
COC polymer offers exceptional transparency, and is very well suited for microscopy!





