In-line hypoxia in cell culture under flow
Compatible with most types of flow controller
Use your current peristaltic, pressure-driven or syringe pump
In line adjustment of oxygen concentration
Precisely control or change the oxygen concentration of your media
Minimize the effects of tubing permeability
Place the in line hypoxia chamber right before your chip

Need a microfluidic SME partner for your Horizon Europe project?
In-line hypoxia in cell culture under flow
Hypoxia Chambers as the field standard
To reproduce hypoxic conditions in cell culture, most researchers use hypoxia chambers. They consist of large pieces of equipment with a tight control of the internal atmosphere so the desired gas partial pressures are diffused into the cell culture media. They are the standard when we talk about hypoxia assays, however, few discuss the limitations of the diffusion approach.
In hypoxia chambers, or any other gas-controlling equipment such as incubators, the atmosphere usually takes minutes to equilibrate to the new partial pressures, but the cell culture media can take hours [1]. Adding that to the fact that the oxygen consumption of cells varies depending on the cell type results in an unknown oxygen concentration in the cellular microenvironment.

A new paradigm of increased complexity
As the field evolves towards more physiologically-relevant systems, as with organ-on-chip and microphysiological systems often under flow, and complexifies, with different cell types in the same microfluidic device, so does the need to better define gas control of the cell cultures.
With that in mind, we decided to move away from hypoxia chambers and develop a module for inline gas control of perfused cell cultures.
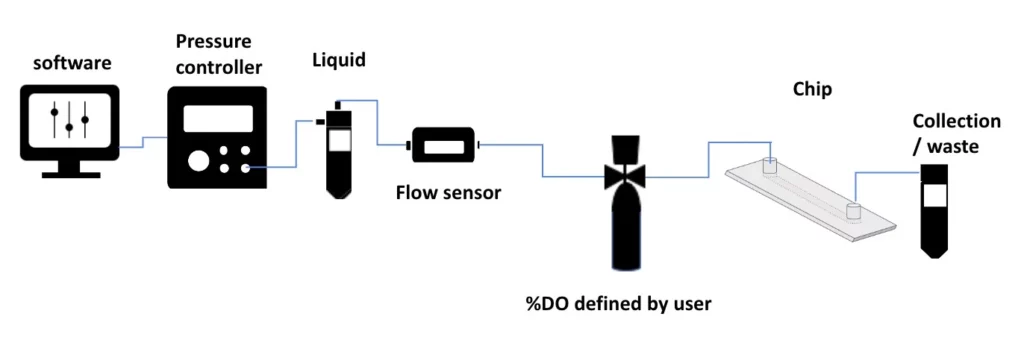
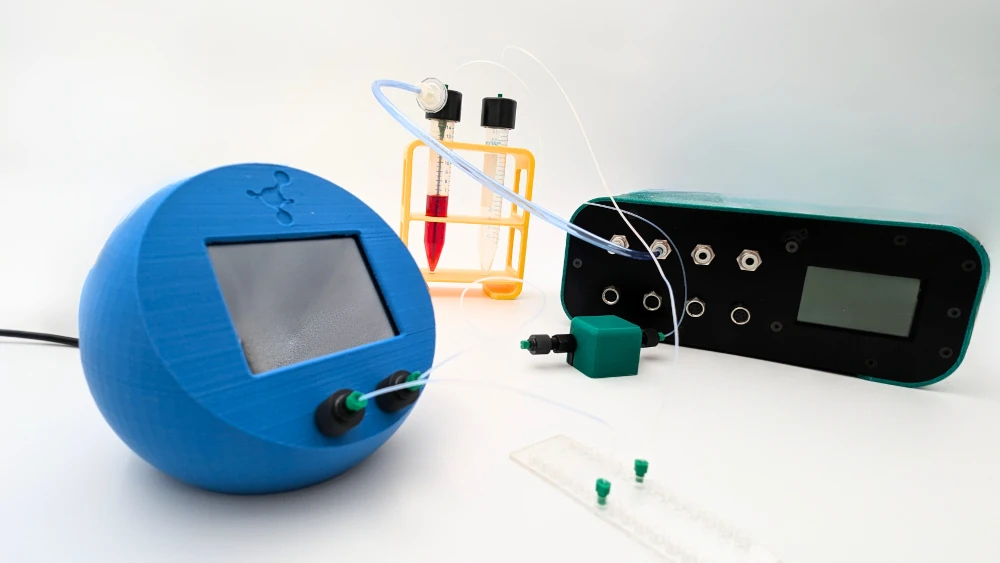
The inline hypoxia chamber pack includes:
Flow sensor (Galileo, MIC)
Cell culture pump
In-line Hypoxia chamber
Reservoirs
Tubings and fittings
Microfluidic chip
User guide
Software (Galileo user interface)
The setup consists of a pressure-driven flow controller and flow sensor to ensure the highest possible accuracy and smoothness of flow profile and our in-line hypoxia chamber that can be easily placed near the microfluidic device to decrease gas exchange between the atmosphere and the media through tubing and connections. The in-line hypoxia chamber is all encompassing, meaning, it allows for control and sensing of gas concentration in the liquid, while avoiding the insertion of bubbles or foam into the system.
More flexible than hypoxia chambers
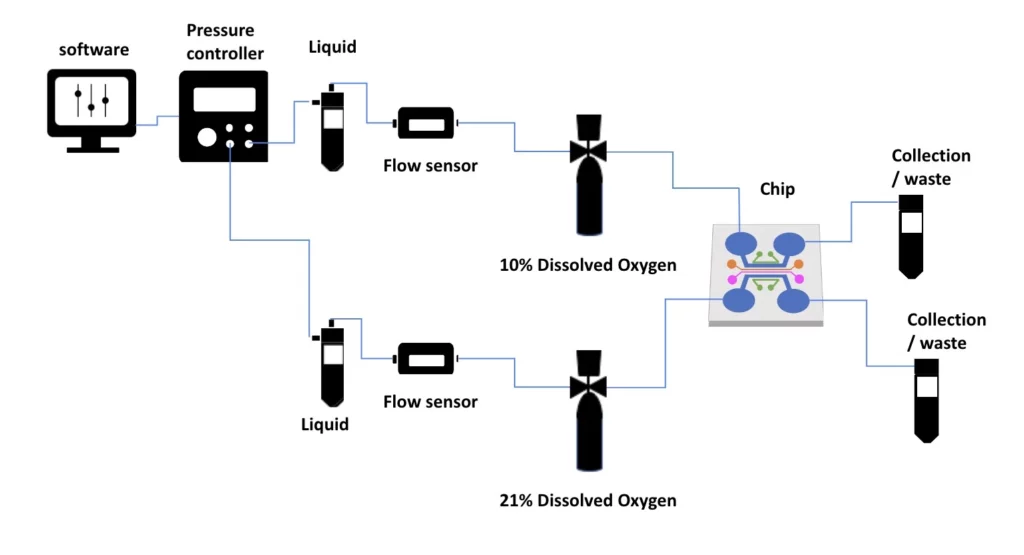
Unlike hypoxia chambers, this system is particularly interesting when there is need for multiple gas compositions within the same experiment, as is the case for gut-on-chip or placenta-on-chip experiments, for example.
References
Pavlacky J, Polak J. Technical Feasibility and Physiological Relevance of Hypoxic Cell Culture Models. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2020 Feb 21;11:57. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2020.00057. PMID: 32153502; PMCID: PMC7046623.
Hypoxia for dynamic cell culture applications
Some biological applications of our hypoxia system include:
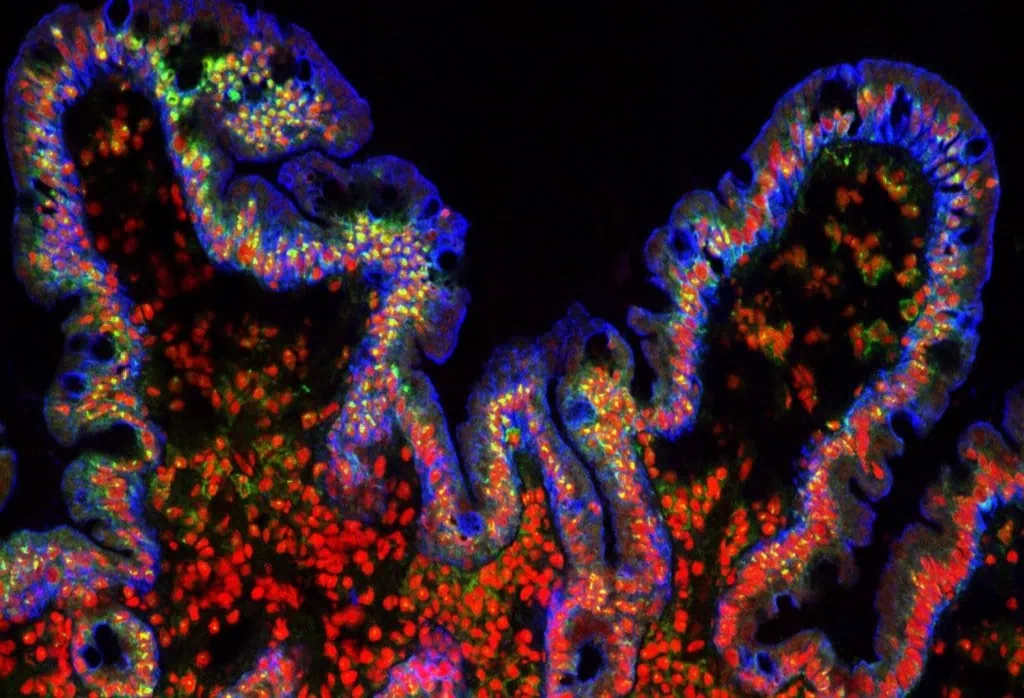
Gut-on-a-chip pack
Intestinal cells coculture under flow, mimicking the gut physiology
✓ All microfluidic pieces included, quick and easy assembly
✓ Dynamic culture conditions
✓ Advanced in viro/ex vivo
Gut-on-chip
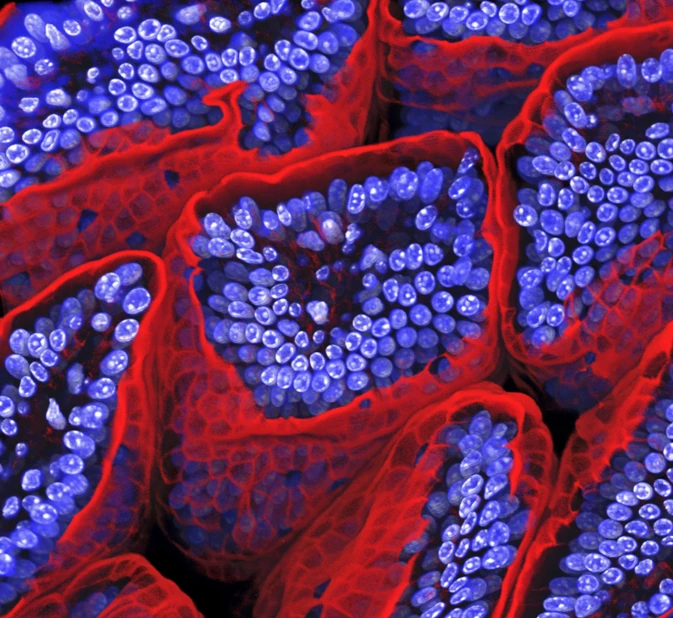
Inflammatory bowel disease model
Automatically collect important markers of IBD in a relevant in vitro model
✓ Uncover cytokine profile changes in time
✓ Mimic pathological conditions of IBD
✓ Tailor sample volume to your analysis
Inflammatory bowel disease model
Blood-brain barrier on chip
Plug-and-play instrument pack for long term BBB on a chip study
✓ Relevant microenvironment
✓ Automatized organ-on-chip perfusion
✓ Plug-and-play microfluidic platform
Blood-brain barrier on chip
Liver-on-a-chip pack
Mimic the liver microenvironment in long term experiments
✓ Improve your reproducibility with physiological culturing conditions
✓ Automated and controlled supply of nutrients in a stable flow
✓ Test different conditions at the same time
Liver-on-chip
Lung-on-a-chip pack
Perform lung research in a physiologically relevant microenvironment
✓ Culture your lung cells in a physiological air-liquid interface
✓ Continuous and controlled supply of nutrients in a stable flow
✓ Stop losing your cell experiment due to clogging
Lung-on-a-chip
Placenta-on-chip
And many more!
In-line Hypoxia chamber technical specifications
Building upon hypoxia chambers as the field standard, the following table summarizes the main specifications of the system.
| Components | Technical specifications |
|---|---|
| Wetted Material | PTFE |
| Dimensions | 10x10x10 cm (control unit) 3x1x1 cm (sensing unit) |
| Admissible Flow rates | 1-100 µL/min |
| Accessible Oxygen Levels | 0-20 %DO |
| Stability of the control | +/- 0.5 %DO |
| Dynamic range of control | 0.5% DO / min |
Cell culture pump technical specifications
The cell culture pump can come with 1 to 4 channels. Each channel connects to a flow sensor with a feedback-loop between pressure and flow rate. Each channel has the following specifications (tested with a set pressure value of 2 bar):
| Characteristics | Specifications |
|---|---|
| Accuracy | -27.75 mbar |
| Air consumption | 0.24 L/min |
| Response time | 140 ms |
| Settling time | 2750 ms |
| Overshoot | Room temperature to 70 oC |
| Temperature accuracy | 0.12 mbar |
Customize your pack
All the instruments are controlled by the same software, allowing workflow automation and easy integration in your program with free available libraries.
Frequently asked questions
Does the in-line hypoxia chamber act as a hypoxia chamber?
In principle yes, hypoxia chambers rely on diffusion to equilibrate gas concentrations in the media. The in-line hypoxia chamber makes this process more efficient.
Are the tubings and connectors impermeable to oxygen?
The standard PTFE tubing is permeable to oxygen, and the connectors in themselves are impermeable but the connection is not. Knowing that, our team has come up with solutions to minimize the entry of atmospheric oxygen into the system.
Which microfluidic chips can be connected to the in-line hypoxia chamber?
The in-line hypoxia chamber can be connected to any microfluidic chip, using the right connectors.
Can the in-line hypoxia chamber be placed inside the CO2 incubator?
The system is intended to replace the need for a CO2 incubator.
What is the maximum flow rate that can be applied?
The system works well with the range of 0-5ml/min.


Funding and Support
The LIFESAVER project, funded by the European Union’s H2020-LC-GD-2020-3, grant agreement No. 101036702 (LIFESAVER), helped develop this pack.
Products & Associated Accessories
FAQ - In-line hypoxia in cell culture under flow
What is an in-line hypoxia chamber and why has it been invented?
In-line hypoxia chamber is a microfluidic assembly that is created to maintain the concentration of oxygen directly within the culture media passing through cells instead of depending on the diffusion of atmospheric gases. It was created to overcome shortcomings of conventional hypoxia chambers, the field standard of simulating hypoxic conditions in the cell culture. Although hypoxia chambers regulate the atmosphere around cell cultures, it is a major challenge: the atmosphere stabilizes within minutes, whereas the cell culture media may take hours to stabilize at the desired oxygen levels. This, together with variation in oxygen consumption rates across cell types, creates uncertainty in oxygen levels in the actual cellular microenvironment. With the development of the field towards more intricate physiologically-relevant models, such as organ-on-chip and microphysiological systems, with many types of cells flowing, this issue has become urgent.
What are the differences between the in-line hypoxia chamber and the conventional hypoxia chambers?
The conventional hypoxia chambers comprise huge equipments that regulate the atmosphere within a confined area and take advantage of the diffusion of gases through the culture medium to access cells. The in-line hypoxia chamber is a paradigm shift because it directly regulates gas concentrations in the flowing medium. Key differences include:
-Location: This is placed close to the microfluidic chip, reducing gas exchange through the tubing.
-Precision: regulates oxygen concentrations in the liquid phase (0-20% dissolved oxygen)
-Speed: 0.5% DO/min dynamic range enables quick changes.
-Flexibility: Allows the use of a variety of gas mixtures in the same experiment, which is critical for models such as gut-on-a-chip (requiring different oxygen levels in the lumen versus tissue compartments) or placenta-on-a-chip (maternal versus fetal oxygen levels).
-Integration: Interacts with flowing cell cultures rather than static cultures.
-Efficiency: Wholesome design-based gas concentration sensor without bubbles and foam.
What does the in-line hypoxia chamber pack contains?
The entire pack includes all that is required in hypoxia experiments under flow:
-Flow sensor (Galileo, MIC): Sensors for measuring flow rates with high accuracy.
-Cell culture pump: A flow controller regulates pressure to maintain smooth flow profiles.
-Gas control and sensing module In-line hypoxia chamber: Gas control and sensing module
-Reservoirs: Culture media.
-Tubings and fittings: Full fluidic connections.
-Microfluidic chip: Cell culture.
-User guide: Instructional setup and operation.
-Software (Galileo user interface): Controls all instruments with the features of workflow automation and free available libraries to integrate.
The control of all components is unified by software, which makes the work easier and open the possibility to make the experiment automatic.
Technical specification of in-line hypoxia chamber?
-Wetted Material: PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene).
-Physical Dimensions:
Control unit: 10x10x10 cm
Sensing unit: 3x1x1 cm
-Performance Specifications:
Admissible flow rates: 1-100 uL/min
Adequate oxygen concentration: 0-20% dissolved oxygen.
Control stability: +-0.5% DO
Dynamic range: 0.5% DO/min (allows quick oxygen changes)
Such specifications make sure that these are controlled to the highest degree possible to meet sensitive cell culture requirements that may need particular hypoxic conditions.
Cell culture pump specifications?
The cell culture pump is supporting 1-4 separate channels, each channel has the flow sensor fed back control. As per channel specifications (test in 2 bar pressure):
Accuracy: -27.75 mbar
Air consumption: 0.24 L/min
Response time: 140 ms
Settling time: 2750 ms
Overshoot: 0.12 mbar
Temperature: Room temperature to 70 °C.
The flow sensor feedback, pressure-based design guarantees highly accurate and continuous flow profiles which is extremely essential in maintaining stabilized oxygen concentrations and healthy cell cultures.
What are the biological applications that are valuable of the in-line hypoxia system?
The system is used in organ-on-chip and microphysiological applications that need the ability to control oxygen:
-Gut-on-a-chip: Recreates the oxygen gradient of an intestinal lumen anaerobic environment and tissue layers in the presence of oxygen.
-Models of inflammatory bowel disease: Research is on the pathology of hypoxia.
-Blood-brain barrier-on-a-chip: mimics brain microenvironmental oxygenation.
-Liver-on-a-chip: Makes hepatocytes zonated with oxygen.
-Lung-on-a-chip: Oxygen control at air-liquid interface.
-Placenta-on-chip: Simultaneously switches between high maternal (higher O2) and fetal (lower O2) oxygen concentrations.
The technology is useful in any dynamic cell culture system that needs hypoxic, normoxic or any other changing oxygen conditions.
What is the mechanism in which the system reduces oxygen contamination by the atmosphere?
An important problem with flow experiments with hypoxia is oxygen permeability using standard PTFE tubing and connections. This is handled by the in-line hypoxia chamber with:
-Strategic location: This can be placed directly in front of the microfluidic chip, and the tubing length reduced to the minimum possible, at which the oxygen in the atmosphere can diffuse into the tubing.
-Engineered solutions: The development team developed special strategies of reducing the entry of oxygen into the atmosphere.
-Imperfect connectors: Connections are not airtight but the system design takes this into consideration.
This positioning method is such that despite the presence of permeable tubing, the media gets to the cells at the desired oxygen level.
Does the in-line hypoxic chamber have the ability to host any microfluidic chip?
Yes, with proper connectors, the in-line hypoxia chamber is universal with respect to microfluidic chips. This is flexible such that researchers can combine the system with:
-Commercial organ-to-chip systems.
-Microfluidic devices are custom-designed.
-Several chip materials and chip geometries.
-Various channel arrangements.
The system is designed to operate at the range of flow rates 0-5 ml/min which is applicable to the majority of microfluidic cell culture applications. Scientists will be able to retain their favorite chip designs with the ability to incorporate advanced oxygen control.
Does the system substitute CO2 incubators?
In-line hypoxia system is aimed at eliminating the use of CO2 incubators in the perfused cell culture experimentation. The flowing media system with built-in oxygen control, unlike static cultures that require CO2 incubators to maintain medium pH and temperature, offers a more stable environment.
-Accurate oxygen blood control.
-The cell culture pump (70 °C down to room temperature) temperature control.
-Stability of the pH of the flowing media by proper buffering.
This removes the limitation of operating in large incubator chambers, and offers more flexibility to the experiment and the accessibility of microscopes.
How can researchers acquire and modify the in-line hypoxia chamber pack?
You can request a quote from our engineers. We will provide specialized assistance such as:
-Customization depends on the needs of the particular experiment.
-Professional advice on the choice of instruments and accessories.
-Tutoring when setting up a dynamic cell culture system.
-Assistance with the integration with existing laboratory processes.
Its unified software control, with easy-to-use programming libraries, enables seamless integration into automated experimental protocols, and the system can be used for both standard and advanced research.

