Quantum Dot Synthesis Pack
Precision-engineered quantum dots for cutting-edge applications
Improved reproducibility
Ensures uniform quantum dot properties
Superior quality control
High PL QYs with narrow size distributions
Precise temperature management
Accurate nucleation and growth regulation

Need a microfluidic SME partner for your Horizon Europe project?
Revolutionizing quantum dot synthesis with microfluidics
Quantum dot synthesis is a revolutionary method for creating nanoscale semiconductor particles with tunable optical and electronic properties. These nanoparticles, ranging from 2-20 nm, are essential for bioimaging, quantum computing, display technology, and photovoltaics. However, achieving scalable, high-quality quantum dot synthesis comes with challenges like reproducibility, precursor mixing, and temperature control [1].
Maintaining uniform size, shape, and composition is crucial, as even slight variations in temperature, concentration, and nucleation timing can lead to inconsistent optical properties [1]. Therefore, achieving high-quality quantum dots for LED displays, solar cells, and biosensors requires precise control over synthesis conditions [1].
Additionally, scaling from lab-scale to industrial production while ensuring high photoluminescence quantum yield (PL QY) and narrow size distribution remains a hurdle [2]. Moreover, temperature fluctuations during the high-temperature nucleation and growth phases can cause non-uniform crystallization, leading to defects and lower efficiency. Similarly, inefficient precursor mixing may result in particle aggregation and reduced fluorescence efficiency, impacting applications like display technology, bioimaging, and quantum computing [3].
From an environmental standpoint, traditional quantum dot synthesis often involves toxic heavy metals like cadmium, lead, and selenium, raising concerns about sustainability and regulatory compliance. Nonetheless, researchers are actively developing eco-friendly quantum dots, such as carbon dots and perovskite quantum dots, which offer high fluorescence with lower toxicity [4].
Our continuous-flow approach offers precise reaction control, improved reproducibility, and reduced material waste, making it an ideal choice for scaling up production [5].
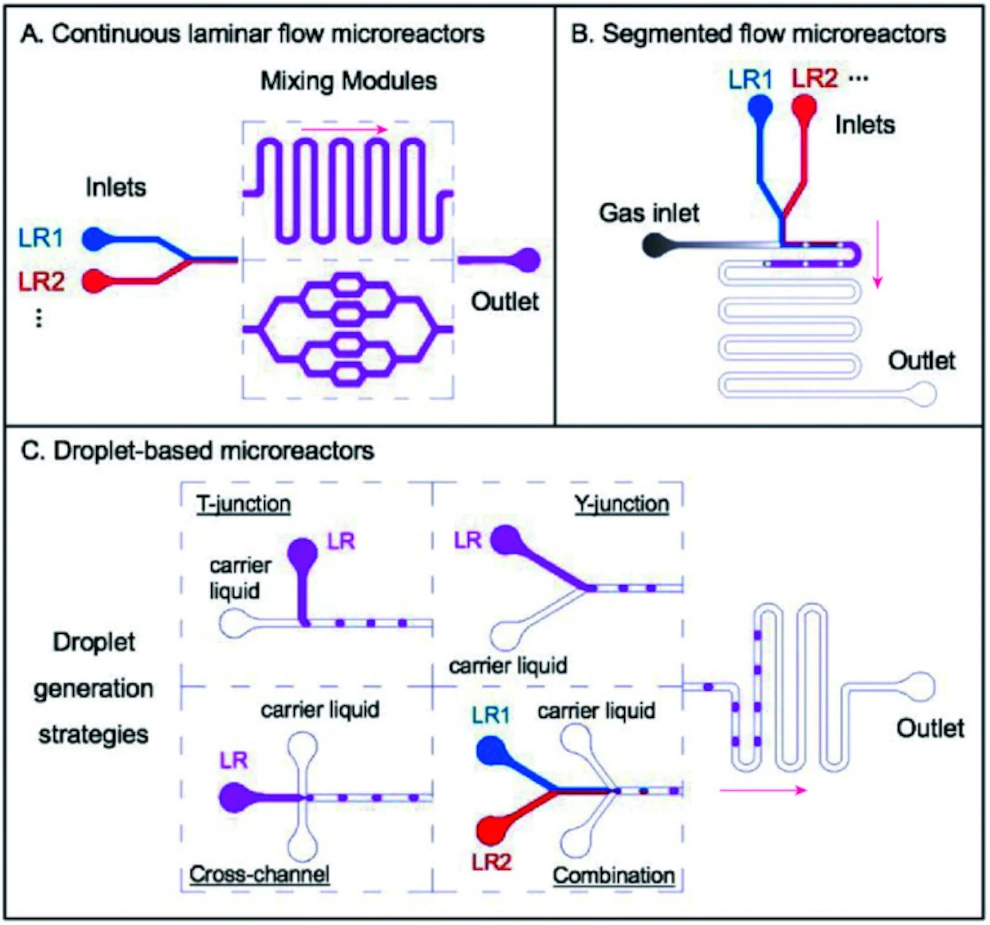
Advantages of microfluidic synthesis over batch methods: This figure highlights the enhanced control and uniformity achievable through microfluidic synthesis of quantum dots, which aligns with the core benefits offered by our Quantum Dot Synthesis Pack.
Adapted from: Shin, D. et al., Nanomaterials (2022), PMC9417800, CC BY 4.0.
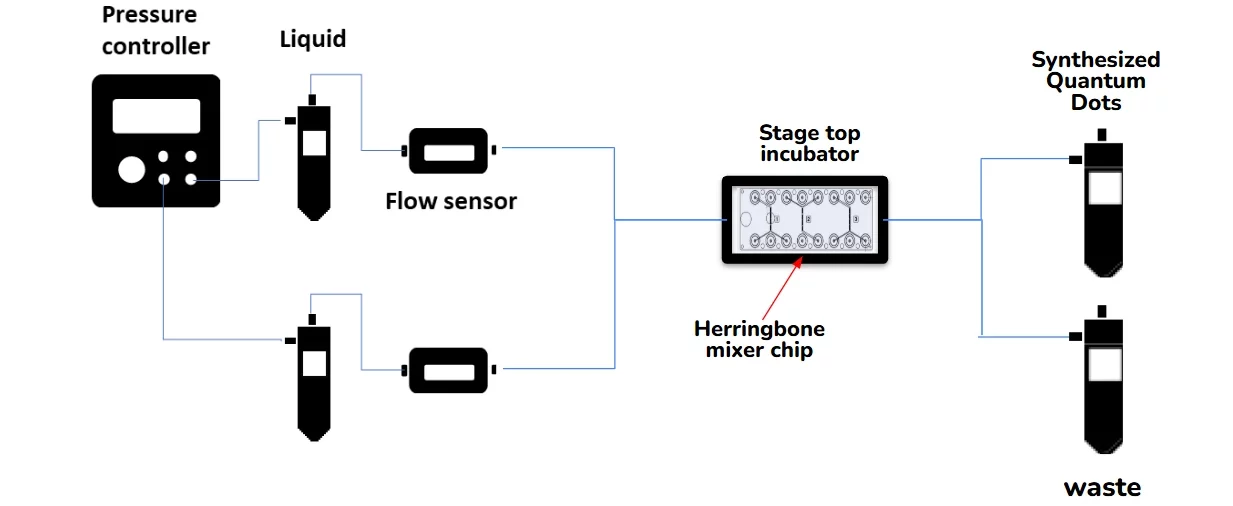
Setup
Flow sensor (Galileo, MIC)
Microfluidic benchtop pump
Stage top incubator
Custom microfluidic chip (e.g., Herringbone mixer chip – microfluidic ChipShop)
Automated sampling system (Optional)
Reservoirs for precursor solutions
Tubings and fittings
Your adapted microscopy setup for real-time monitoring
Collection vials
Your control software for integrated system management
References
Image:
Квантовые_Точки-Quantum_Dots, Wikimedia Commons
Text:
Peng, X., Schlamp, M. C., Kadavanich, A. V., & Alivisatos, A. P. (1997). Epitaxial growth of highly luminescent CdSe/CdS core/shell nanocrystals with photostability and electronic accessibility. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 119(30), 7019–7029.
Large Scale Synthesis of Red-Emitting Quantum Dots for Efficient Light-Emitting Diodes. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces.
Controlled mixing during colloidal quantum dot synthesis: A proxy for reproducibility. Chemical Engineering Journal.
Eco-Friendly and Sustainable Pathways to Photoluminescent Carbon Quantum Dots. MDPI Nanomaterials.
Redefining Quantum Dot Synthesis with Additive-Manufactured Continuous Flow Reactors. MDPI Metals.
Compatibility and applications
- Perovskite quantum dot synthesis
Fine-tune growth conditions for maximal lipid production. - Carbon dot synthesis
Utilize the system to produce carbon dots, fluorescent nanomaterials with applications in bioimaging and sensing. - Nanoparticle functionalization
Precisely control surface modifications of quantum dots for targeted applications. - High-throughput screening
Test engineered strains under highly controlled flow and nutrient regimes. - Biosensor development
Integrate quantum dot synthesis with biosensor fabrication for immediate testing and optimization.
Flow sensor technical specifications
Flow rate ranges: For example, flow rate ranges with <5% accuracy:
- 0.5 – 60 µL/min
- 2 – 150 µL/min
- 40 – 1200 µL/min
- 0.5 – 10 mL/min
Note that the range can be customized depending on working fluid properties (viscosity, etc.)
Calibrated liquids: aqueous media (others are possible upon request)
Wetted materials: PEEK, steel, fluorosilicone, perfluoropolyether resin
Internal volume: approx. 40 µL (variable depending on the used configuration range)
Operation pressure: up to 3 bar gauge pressure
Maximum pressure rating: up to 6 bar gauge pressure
Software operability: standalone GUI for data visualization and logging; optional Python API
Microfluidic benchtop pump technical specifications
| Pressure control | |
|---|---|
| Pressure stability | 0.2 mbar |
| Air flow rate | 0.1 L/min at atmospheric pressure Possibility to work with higher air flow rates by reducing the pressure range |
| Flow control | |
| Microfluidic flow sensor | Monitoring and feedback loop flow control available |
| Flow rates | From 0.1 µL/min to 5 mL/min |
| Liquid compatibility | Non contact pump
Any aqueous, oil, or biological sample solution |
| Electrical connection | |
| USB connection | USB C |
| Sensor connection | One M8-4 pins connector available per channel |
Stage top incubator technical specifications
| Characteristics | Specifications |
|---|---|
| Dimensions (mm) | 30.5 x 130 x 168 (h x w x l) |
| Base K- Frame | 3.5 x 110 x 160 (h x w x l) |
| Dimensions of internal usable space | 25 X 89 x 130 (h x w x l) |
| Dimensions of the bottom glass (ITO glass) | 1) 72 X 110 with a thickness of 1.1 mm 2) 50 x 25 with a thickness of 0.6mm 3) 50 x 22 with a thickness of 0.12 mm |
| Temperature range | Room temperature to 70 oC |
| Temperature accuracy | ± 0,5 oC |
| External material | Aluminum and ITO glass |

Frequently asked questions
Can our platform be customized for different types of quantum dots?
Yes, the platform’s versatility allows for adaptation to various quantum dot materials and synthesis protocols.
What are the benefits of real-time monitoring during synthesis?
Real-time monitoring enables immediate adjustments to synthesis parameters, ensuring optimal quality and consistency.
Is the system scalable for industrial production?
While our system is optimized for research and small-scale production, it provides critical insights into process parameters that can be transferred to larger continuous-flow reactors.
How can we help your experiment?
This pack is in beta testing phase. So, although the instruments are not fully industrialized, we can provide extensive support as part of our beta testing program. Get in touch to see if you are eligible.


Funding and Support
Products & Associated Accessories
FAQ - Quantum dot synthesis pack
What does the Quantum Dot Synthesis Pack do?
It is a combined microfluidic system designed to generate high-quality quantum dots, with synthesis conditions carefully controlled to produce reproducible, high-quality results, and scaling easily achieved between lab and industrial scales.
What are quantum dots, and what is their significance?
Quantum dots are small (2-20 nm) particles of a semiconductor with quantum confinement, which have tunable optical and electronic properties. They find important applications in bioimaging, LED displays, solar cells, biosensors and quantum computing.
Which are the key challenges that the pack deals with?
The pack addresses some of the main synthesis obstacles:
Control over reproducibility and uniform size/shape,
Exact temperature control in the nucleation and growth,
Efficient mixing of the precursors avoiding aggregation,
The ability to scale between research and production volumes,
Lessening of the toxic heavy metal use (e.g. cadmium, lead, selenium).
What is the benefit of using the microfluidic method in the synthesis of quantum dots?
Microfluidic technology offers the advantages of ease of operation, high heat and mass transfer rates, and control over reaction parameters, which are superior in terms of uniformity and batch-to-batch reproducibility compared with conventional bulk synthesis methods.
What are the major technical requirements of the platform?
Minimal flow rate: 0.5-10 mL/min (adjustable to fluid viscosity),
Flow rate accuracy: <5%,
Wetted material: PEEK, steel, fluorosilicone, perfluoropolyether resin,
Internal volume: ~40 uL (variable),
Operation pressure: to 3 bar (maximum 6 bar),
Software: free-standing GUI including Python API.
What comes with the set up (what is optional)?
The reference arrangement is constructed on:
An MIC (Galileo line) microfluidic flow sensor.
A benchtop fluidic micro-pump.
A stage top incubator (controlled temperature up to 70 °C)
A microfluidic chip (e.g. a herringbone mixer design) designed from scratch.
Reservoirs, tubings/fittings, collection vials.
Your microscopy / monitoring scheme of real-time observation.
Your integrated system management control software.
Automated sampling is specifically identified as optional, which is important when you are doing kinetics or screening, and do not need to supervise the collection step.
What are the most important technical requirements that researchers tend to request initially?
The following are the production numbers that determine practicability in most laboratories:
Flow sensor (examples of ranges with less than 5% accuracy)
0.5 to 60 uL/min
2 to 150 uL/min
40 to 1200 uL/min
0.5 to 10 mL/min
Other flow-sensor specifications: default calibration in aqueous media, wetted materials (PEEK, steel, fluorosilicone and perfluoropolyether resin, optional wetted in other liquids) internal volume in the order of 40 uL (depending on configuration), operating pressure 3 bar gauge (maximum pressure 6 bar gauge), configuration Use case Typically installed in places where there is a liquid flow and the flow velocity is required to be measured by an electrical device (such as a rheometer or rheostat). It has a visualization/logging standalone GUI and optional Python API.
Benchtop pump
Pressure stability: 0.2 mbar
Air flow rate: 0.1 at atmospheric pressure (greater possible with a narrower range of pressure)
Flow rates: 0.1 uL/min to 5 mL/min
Liquid compatibility non-contact pump: compatible with aqueous, oil and biological sample solutions.
USB-C connector; per channel sensor connector M8-4 pin connector.
Flow control in terms of monitoring and feedback loops can be used when combined with the flow sensor.
Stage-top incubator
Temperature: 25 to 70 °C.
Temperature accuracy: +-0.5°C
(And Geometry constraints that are important when you are integrating a particular microscope or chip holder.)
What supported calibrated liquids and materials does the system have?
The standard set-up is adjusted to aqueous media, and other fluids can be requested. Wetted media are chosen to make sure that they are chemically compatible with reactive quantum dot precursors.
Is it possible to put the platform on other types of quantum dots?
No, the platform is not restricted in terms of the types of quantum dots materials and synthesis procedures.
What are the downstream applications which the pack supports?
The pack is also compatible with biosensor fabrication for real-time testing and optimization. Expansive target markets are LED displays, photovoltaic, bioimaging, and quantum computing.
What is the comparison of microfluidic mixing with the traditional bulk techniques?
Miniaturization of the reaction vessel, coupled with a high degree of mixing, could yield better performance than conventional bulk-scale processes and provide more monodisperse particles with narrower size distributions.

