Noise-Free Patch Clamping
Smooth and stable flow
No noise caused by pulsatile flow
Control over low flow rates
Easily control flow rates below 1µL/min
Easy reversible flow
Switch between vacuum and flow

Need a microfluidic SME partner for your Horizon Europe project?
Patch clamp: a short introduction
Briefly, a glass electrode containing the appropriate medium is placed at the cell membrane. Applying suction to the electrode will form a seal with the membrane. If the membrane remains intact, it is possible to record the activity of ion channels present in the patch of membrane that is in contact with the electrode. If the membrane is intentionally broken, whole-cell readings become possible, with the electrode acting as part of the cell. It is also possible to control the voltage or the current applied to the cell and record its responses, or detach a particular patch of membrane and study different interactions with the electrode.
Current patch clamping setups
This single-cell interaction is extremely sensitive to fluctuations in flow, and the seal can be lost due to the pulsatile nature of the peristaltic pump motion.
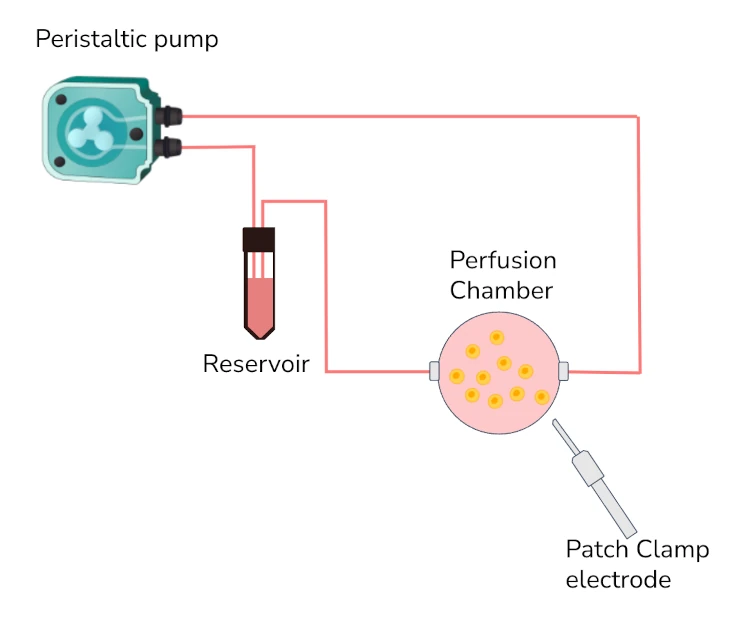
An improved protocol for patch clamping
Flow rates are easily controlled through its screen, going below 1 µl/min, for localized measurements, or higher, for whole cell experiments. It is also possible to reverse the flow if the goal is to release the cell without breaking the membrane.
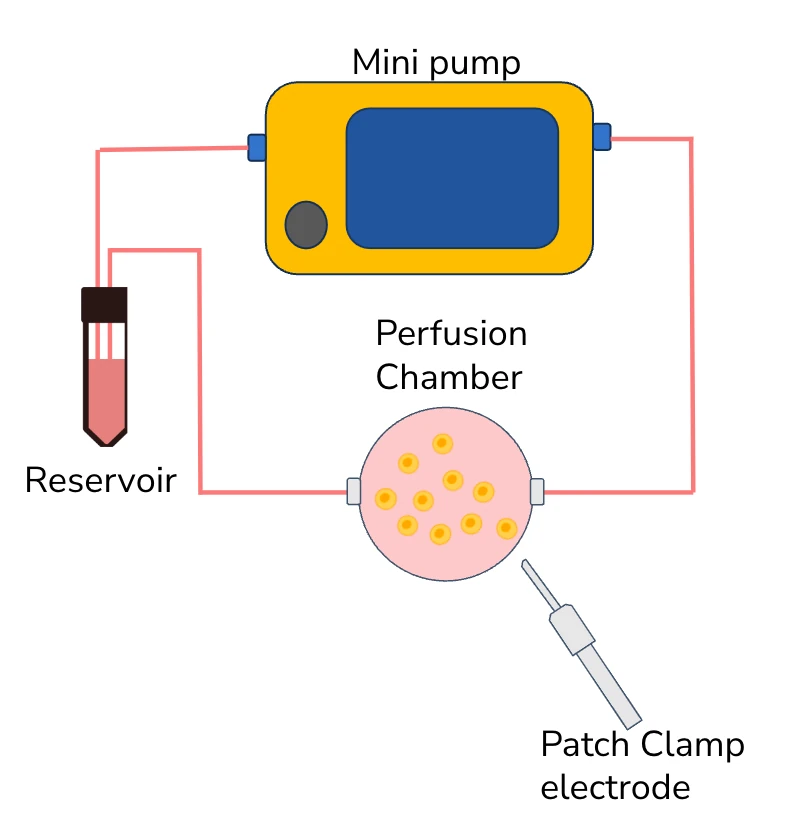
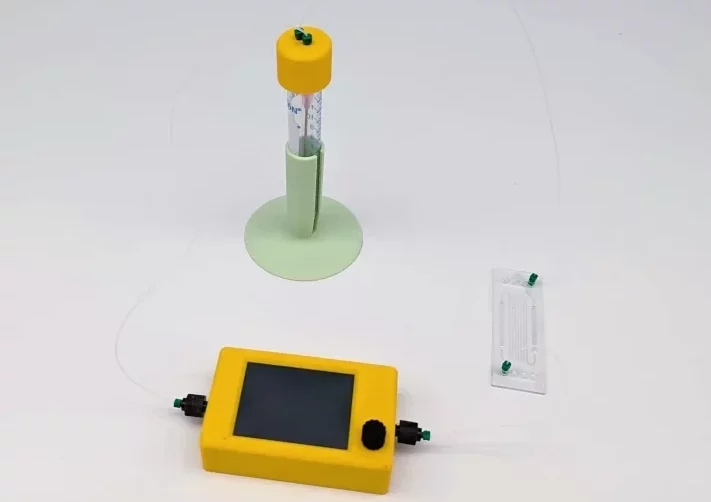
Setup
Mini pump
Reservoirs
Glass electrode
Patch clamp amplifiers and readers
The main aim of our setup is to change as little as possible from the conventional technique, with few adjustments to be done, while benefitting from considerable improvements. Thus, the mini pump was designed to simply replace the peristaltic pump, without the need to change or adapt anything else.

Mini pump applications
Some applications of our microfluidic cell culture system include:
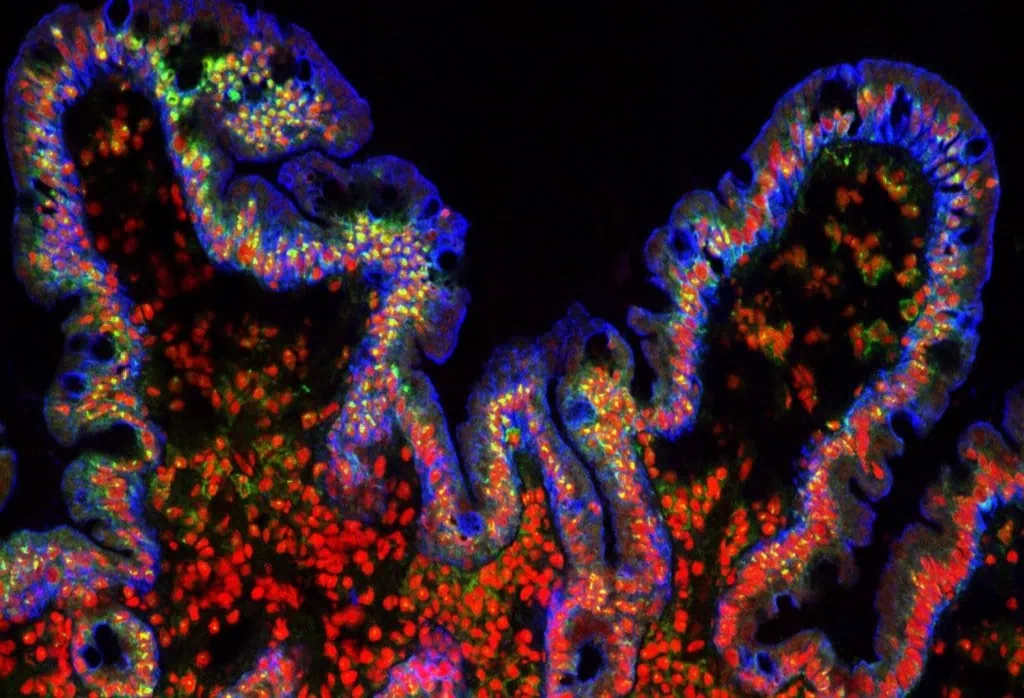
Gut-on-a-chip pack
Intestinal cells coculture under flow, mimicking the gut physiology
✓ All microfluidic pieces included, quick and easy assembly
✓ Dynamic culture conditions
✓ Advanced in viro/ex vivo
Gut-on-chip
Blood-brain barrier on chip
Plug-and-play instrument pack for long term BBB on a chip study
✓ Relevant microenvironment
✓ Automatized organ-on-chip perfusion
✓ Plug-and-play microfluidic platform
Blood-brain Barrier on Chip
AFM live cell imaging
Electrophysiological studies, such as voltage clamp, whole cell patch clamp, current clamp, etc.
And many more!
Patch clamping with the mini pump
Considering that the setup remains mostly the same as a conventional patch clamping experiment, here we focus on the the technical specifications of the mini pump:
| Technical Specifications | |
|---|---|
| Flow rates | down to 1 µL/min |
| Wetted material | Polyphenylsulfone (PPSU) or stainless steel |
| Operating Temperature | 5-50 °C |
| Maximum pressure | up to 500 mbar |
Frequently asked questions
What is the working principle of the mini pump?
The mini pump has a piezoelectric mechanism.
Can the mini pump be used near/on top of a microscope stage?
Yes, the mini pump was designed to withstand high temperatures and humidity. It could be placed inside an incubator if needed.
What is the maximum flow rate that can be applied?
The system works well with the range of 0-5ml/min.



Funding and Support
The BIOPROS project results helped develop this instrument pack, with funding from the European Union’s Horizon research and innovation program under HORIZON-CL4-2021-DIGITAL-EMERGING-01-27, grant agreement no. 101070120.
Products & Associated Accessories
FAQ - Patch clamping
Basic definition of patch clamping?
Patch clamping is an electrophysiological method used to quantify ionic currents across a cell or a patch of cell membrane. The method is particularly useful for investigating excitable cells, including neurons, cardiac cells, and muscle fibers. Practically, a glass electrode filled with a suitable medium is placed at the cell membrane, and a suction is applied because it makes a tight seal with the membrane, which researchers call a gigaohm seal because it has a very high electrical resistance.
What kinds of measurements is patch clamping capable of?
Patch clamping has a number of experimental configurations:
-Cell-attached mode: When the membrane is intact, researchers can measure the activity of ion channels in the membrane patch in contact with the electrode.
-Whole-cell recording: When the membrane is deliberately damaged, the electrode is inserted into the cell interior, and whole-cell current measurements can be made.
-Voltage or current control: It is possible to control the voltage or current applied to the cell and measure its responses.
-Excised patches: The patches of a specific membrane may be cut away and analyzed in single response to a variety of interactions with the electrode.
What are the constraints of the existing patch clamping systems?
Conventional patch-clamping experiments use peristaltic pumps to perfuse cells in the recording chamber, thereby providing optimal physiological conditions. The method is, however, not without serious challenges:
-Pulsatile: Peristaltic pumps cause noise in sensitive electrical records due to the mechanical motion that causes pulsations in the flow.
-Seal instability: The gigaohm seal between the cell membrane and the glass electrode is very sensitive to flow variations. Pulsatile flow may cause loss of seal parts, ending the experiment prematurely.
-Poor resolution: Peristaltic systems are difficult to operate in the lowest flow rate control (below 1 uL/min).
-Large machines: Peristaltic pumps occupy a lot of bench space near the microscope.
What is the enhancement of patch clamping experiments by the Mini Pump?
The Mini Pump overcomes the classical constraints in the following:
-Constant, aqueous flow: Provides smooth flow with no pulse with the fragile gigaohm seal intact and enhances the accuracy of the measurements made.
-Exact low flow control: It easily attains low flow rates down to 1 uL/min to local measurements or higher to whole-cell measurements.
-Reversible flow: It is capable of switching between forward flow and vacuum allowing the release of cells without cell rupture.
-Small size: The small size enables it to be conveniently placed near the microscope without taking too much space on the bench.
-Flexible reservoir compatibility: Can easily form a range of different volumes between 1.5 ml Eppendorf tubes up to 1 L bottles.
-Easy to use: There is one inlet and one outlet, and the control is made via a handle interface on the screen.
How does the Mini Pump work?
The Mini Pump uses a piezoelectric system as opposed to mechanical rollers or gears. This piezoelectric actuation removes the mechanical movement that causes pulsatile flow of peristaltic pumps to provide smooth and continuous flow which is optimal to delicate electrophysiological measurements.
What is the difference in the experimental setup with experimental patch clamping?
The configuration does not need many changes:
-Unchanged Standard Components:
-Glass electrode
-Patch clamp readers/ amplifiers.
-Cell chamber
-Microscope system
-Tanks of perfusion solutions.
-Single Replacement:
It can replace the peristaltic pump with Mini Pump which does not need other components to be adapted.
It is a plug-and-play solution that is familiar with the traditional methods but provides significant gains in stability in measurements and seal integrity.
What other uses can be made of the Mini Pump?
In addition to patch clamping, the Mini Pump can be used on other sensitive cell culture as well as imaging applications:
-Gut-on-a-chip: Intestinal cell fluidic co-culture.
-Blood-brain barrier on chip: Automated control of BBB studies in the long-term.
-AFM live cell imaging: Atomic force microscopy requires vibration-free flow
-Electrophysiological experiments: Voltage clamp, current clamp, and other requirements of stable perfusion.
-Organ-on-chip systems: Organ-on-chip systems are microfluidic cells culture systems that demand a pulsation-free flow that is precise.
Will the Mini Pump be capable of working under challenging environments?
The Mini Pump was actually created to withstand high temperatures and humidity. It can be:
-Positioned directly on top of, or close to, the microscope stage.
-Worked within CO2 incubators (as required).
-Applied in temperature-controlled settings between 5-50 °C.
-Integrated into complex multi-instrument setups
This environmental strength renders it applicable to various experimental setups.
What is the method that researchers use to acquire the Mini Pump to patch clamp?
Researchers may request a quote by visiting our website or contacting us directly. We provide:
Standard Mini Pump specifications.
Technical advice to be incorporated into current patch clamp systems.
Flow parameters optimization is supported to optimize flow parameters to specific cell types.
Recommendations on the choice of reservoir and experimental procedures.
The simple replacement design reduces the time of setup and maximizes experimental gains in the stability of seals and quality of measurement.

