Kidney disease multifunctional diagnosis by multiplex qPCR: Multidet
Author
Christa Ivanova, PhD
Publication Date
September 14, 2017
Status
Keywords
Multiplex qPCR
Optofluidic chip
FASTGENE technology
Point‑of‑Care Test
Kidney disease biomarkers
bacterial glomerulonephritis
Chronic kidney disease
Your microfluidic SME partner for Horizon Europe
We take care of microfluidic engineering, work on valorization and optimize the proposal with you
The MULTIDET project, aiming to develop a kidney disease diagnosis tool, is supported by INNOSUP-02-2016 program, in the context of European SME innovation associate action.
Kidney disease diagnosis by qPCR: introduction
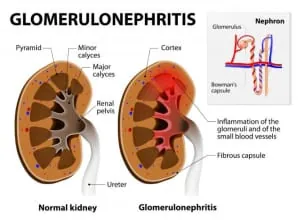
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) affects 10% of the population worldwide, and sporadic cases of acute nephritis, if not detected early enough, may also progress to a chronic form.
In particular, glomerulonephritis (GN) represents the leading cause of chronic renal failure (25%).
GN comprises several kidney diseases, mainly characterized by inflammation of the glomeruli, which are the units involved in filtration or the small blood vessels surrounding the kidneys.
As it is not strictly a single pathology, its presentation depends on the specific disease, and rapid and accurate diagnosis is crucial because the outcome and treatment differ in different conditions.
Despite several cheap traditional tests based on the analysis of urinal and blood samples, no technology is currently available to measure DNA biomarkers associated with infective GN simultaneously and perform immunological and cytological analyses.
Kidney disease diagnosis by qPCR: project description
The development of fast multiplex quantitative PCR (qPCR) technologies offers a unique opportunity to propose a Point of Care Test (PoCT) to perform new multifunctional cheap diagnostics of chronic kidney disease.
One of our main R&D projects was FASTGENE, the technology at the heart of the MULTIDET project. FASTGENE is a microscopic optofluidic chip whose temperature is controlled by a microthermal exchanger and can carry out ultrafast qPCR, conserving yield, sensitivity, and selectivity of the gold standard qPCR.
Within the MULTIDET project, we aim to develop and optimize multiplex ultrafast qPCR for diagnosing bacterial GN from urine samples, determining microorganisms’ identity and pattern of resistance/susceptibility to antibiotics.
Moreover, the possibility of performing an integrated analysis of immunological and cellular biomarkers will allow for the differential diagnosis of infective and non-infective GN.
This project has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under grant agreement No 739688 (Multidet project).


Check our Projects
FAQ – Kidney disease multifunctional diagnosis by multiplex qPCR: Multidet
Simply stated, what did MULTIDET mean?
A small, point-of-care workflow that simultaneously detects numerous targets of interest in kidney disease, such as pathogens, resistance genes, and host-response transcripts, with ultrafast multiplex qPCR, such that by the time the clinician makes the visit, they can know the difference between infectious and non-infectious glomerulonephritis, not days later.
When was it broadcast and which programme?
As an action of Horizon 2020 (grant agreement No. 739688) between 15 September 2017 and 14 September 2018. Small-scale, narrow scope, prototypical deliverables.
Why is it better to multiplex qPCR kidney disease as compared to single-analyte tests?
Since the kidney presentations are overlapping, no single marker is reliable. Multiplexing distorts a great number of questions into a single run: What organism? What are the resistance determinants? What is the patient’s immune response? This augments the yield of the diagnosis and reduces the amount of unnecessary empiric treatment.
What were the priorities of samples and targets?
Urine indicator of pathogen: and resistance indicators; blood indicators of systemic inflammatory/host-response indicators. Standard target panel types include organism ID, super-resistant genes (to direct antibiotic selection), and a few immune markers that indicate sterile inflammation.
What is considered fast in this regard?
The design envelope was set at ≥30, with a turnaround time of 1 consultation window (approximately 10-15 minutes of thermocycling and little hands-on time). The Microfluidics closed-cartridge maintains its safety from contamination and is easy to operate.
What are the readout decisions that it directly affects?
Three urgently needed: (1) rule-in of bacterial GN to support the use of antibiotics, (2) avoidance of first-line drugs postulated to fail due to resistance phenotypes, and (3) rule-out infection to shift to non-infectious GN work-ups and nephrology referral. That will save time-to-treatment days down to minutes.
What is the exact location where microfluidics finds its place?
Unified nanolitre-to-microlitre reactions, high-speed heat transfer, inbuilt nucleic-acid preparation, and closed paths, which avoid carryover. It is called microfluidics, which allows achieving many targets in minutes, not just in a benchtop lab.
What was the technical definition of success?
A self-contained cartridge and control electronics supporting multiplex qPCR with internal extraction/inhibition controls; analytical coverage of ≥90% of the expected pathogens and high-resistance determinants; and a clinical feasibility set on 150-300 real specimens- mapping cleanly between TRL 4 and TRL 6.
I am developing a Horizon Europe consortium- where should MIC be placed outside this project?
MIC is a microfluidics SME specializing in regularly participating in EU consortia to provide hardware, automation, and measurement components for complex bioassays. We prepare offers together, model work packages based on prototype deliverables, and risk-proof manufacturable designs. Consortia incorporating MIC prototype-first model usually claim success rates that are twice the official baseline at similar calls- a trend we put down to obvious technical way, believable milestones, and early demonstrators.