Microfluidics and optics for single cell observation on a chip: PROCHIP
Author
Christa Ivanova, PhD
Publication Date
September 01, 2018
Status
Keywords
microchannel flow control
Lab-on-a-chip
optofluidics
epigenomic reprogramming
tumor heterogeneity
chromatin alteration
on-chip microscopy
Your microfluidic SME partner for Horizon Europe
We take care of microfluidic engineering, work on valorization and optimize the proposal with you
In the case of cancer, tumor progression mainly relies on epigenomic reprogramming, allowing infected cells to adapt to foreign environments.
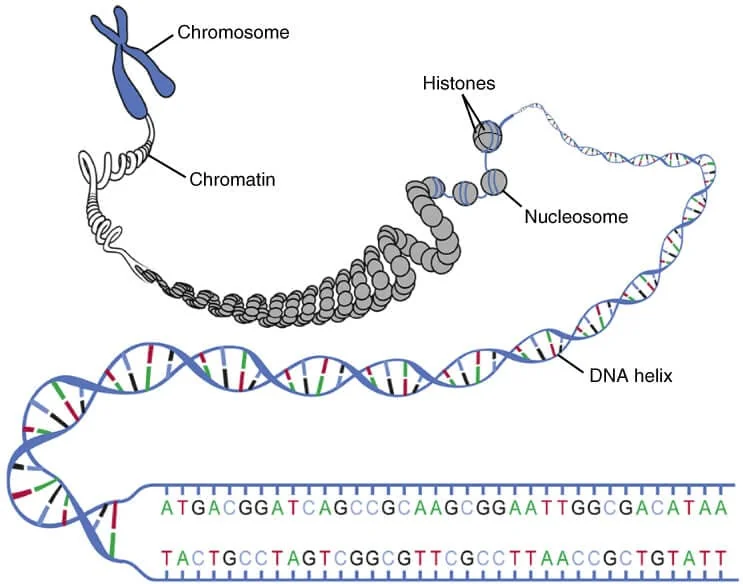
One manifestation of this reprogramming is chromatin alteration.
An efficient tool for high-throughput single-cell observation is needed to study this phenomenon.
Single cell observation on a microfluidic chip: introduction
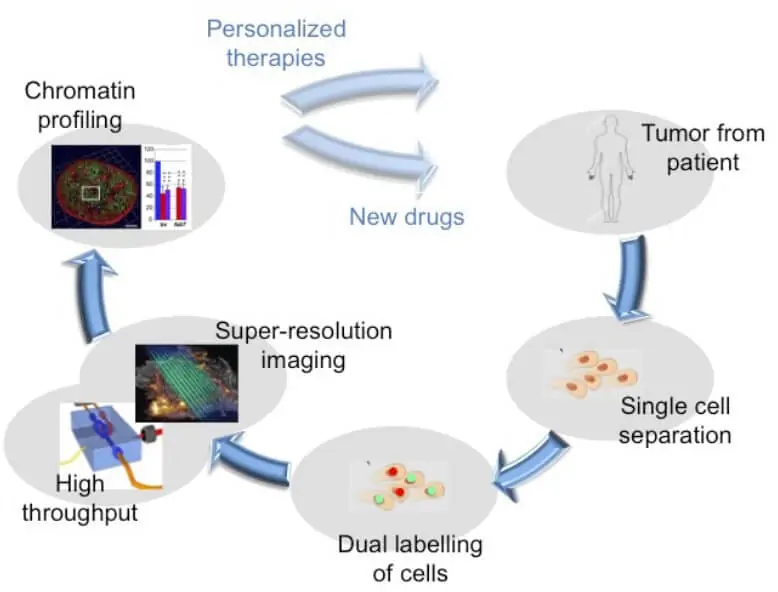
Understanding the 3D organization of cancer-associated chromatin domains should thus help to unravel tumor heterogeneities and develop targeted therapies.
As no microscopic technique is currently available to characterize chromatin structures at the single-cell level, this project aims to develop a high-throughput super-resolution microscope to quickly analyze chromatin in many cells.
Imaging will be performed in a one cm² microfluidic glass chip where the cells will flow, and each single cell will be scanned automatically.
All optical components necessary for the observation will be integrated into the microfluidic chip.
Single cell observation on a microfluidic chip: our role
In this European consortium, we will bring our expertise in fluid handling for microfluidics to acquire precise data for flow velocities corresponding to 100 cells/min.
The microfluidic flow controller, coupled with an innovative flow sensor and image analysis, will fine-tune the flow rate to optimize cell circulation into the chip and enable single-cell efficient detection.
A feedback loop will be integrated to adapt the imposed pressure in real time to keep the cell frequency constant.
This project has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under grant agreement No 801336 (PROCHIP project)


Check our Projects
FAQ – Microfluidics and optics for single cell observation on a chip: PROCHIP
Which scientific gap does the PROCHIP fill?
The main focus of tumor evolution is chromatin architecture, which is not analyzed by most microscopes due to a lack of resolution or throughput. PROCHIP aims to fill this gap: the concept of super-resolution images with a single cell per image, but extending it to a thousand cells per experiment instead of a few.
What are the main concepts of the platform?
Cells are directed around an on-chip optical path through a compact, one-square-centimeter glass microfluidic chip to have each cell scanned automatically as it passes through the chip. The trick is co-design: the set cell position and speed are set by the fluidics; the integrated optics provide an image of high fidelity without halting the sample.
What is the rationale for the in vitro use of the BBB-on-chip instead of animal models?
Since animal BBB responses are not typically aligned with human data, the time/cost footprint is substantial. The organ-on-chip pathway provides you with regulated shear stress and human cell interfaces together with readouts of reproducible barriers, and significantly reduces the use of animals. It iterates more quickly, organization space is cheaper, and it is closer to the target physiology.
What is the definition of the high-throughput we are speaking about?
Nominal flow conditions are set to approximately 100 cells per minute; approximately 6000 cells per hour, and the frequency is maintained constant through closed loop control. This is sufficient to transition to statistical-based, single-cell chromatin readouts, which are based on anecdotal, low-N snapshots.
What is the reason to incorporate optics in the chip as opposed to utilising a normal microscope?
Locating the optics within the microfluidic stack reduces the optical path, eliminates drift in alignment, and gives the imaging geometry reproducible between runs. It also allows a small footprint instrument in which fluidic and optical tolerances are generated at design time.
What are the most important partners in the biological sphere?
The development of the BBB cell culture and barrier architecture on which the chip is fabricated was pioneered by Finnadvance, which is currently known as Akita. MIC and Akita are developed shoulder-to-shoulder, so that biological fidelity and fluidic realism develop together.
What is the practical method of stability in the flow?
An experimental flow sensor is connected to a microfluidic controller of pressure, as well as the image-analysis loop. In case there is a drift in the cell frequency detected, the controller adjusts the inlet pressure in real-time to put the stream in the setpoint, very important in preventing motion blur and uneven exposure.
What are the biological questions that can be answered by PROCHIP?
The system is configured to support single-cell chromatin organization studies on oncology but primarily those in which heterogeneity is mediated by epigenomic reprogramming. More generally, any study that requires super-resolution snapshots across large populations of cells is natural, e.g., cell cycle staging, perturbation screens, and response profiling.
What are the specifications for single-cell observation on a microfluidic chip?
Chip area: Glass microfluidic device, area of chip, ca. 1 cm².
Target cadence: Nominal = 100 cells/min.
Mode: continuous flow, and every cell was scanned automatically.
Control: frequency of image-derived frequency (frequency-adjusted closed-loop pressure) adjustment.
Why do you want to include a specialized SME such as MIC in your Horizon Europe proposal?
Because execution matters, a microfluidics SME shortens the process of turning an idea into a prototype before delivery to the customer by handling in-house creation, manufacturing, programming, control, and testing. The placement of MIC as the microfluidic work-package within our experience with consortia across Europe doubles the likelihood that the proposal will succeed as compared to the overall approach of public call, and it reduces the riskiness of engineering milestones during the grant.