Air-liquid interface and optimized cell culture substrate for a microfluidic lung-on-a-chip application
Author
Lisa Muiznieks, Postdoc
Publication Date
October 05, 2019
Keywords
Lung-on-a-chip
disease modeling
Organ-on-a-chip
air-liquid interface
cell culture

Need advice for your lung-on-a-chip model?
Your microfluidic SME partner for Horizon Europe
We take care of microfluidic engineering, work on valorization and optimize the proposal with you
An introduction to gas exchange at the air-liquid interface of the lung
The lung is the main organ of respiration, whose function is to facilitate gas exchange in and out of the bloodstream. Air is transported down the bronchial tree and into alveolar sacs, where gas exchange occurs across the air-blood barrier with the capillary lumen.
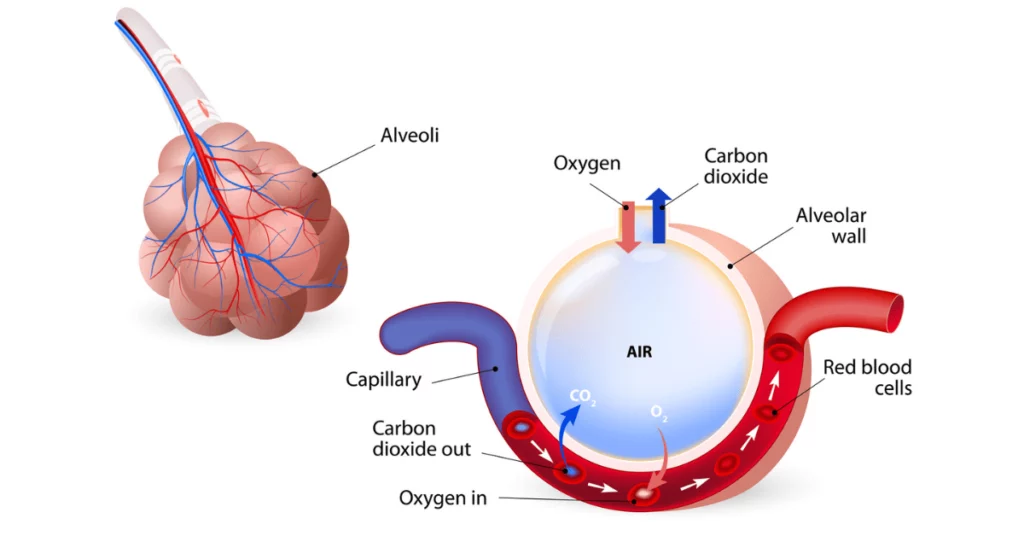
Bronchial cilia line the respiratory tract, and their beating moves mucus and dust up the airway. The alveolar sac is lined with alveolar epithelial cells that share a basement membrane with underlying vascular endothelial cells, forming a thin air-liquid interface.
Stresses on alveolar epithelial cells enhance phospholipid (pulmonary surfactant) production, which improves barrier function by reducing the surface tension of alveoli walls.
Download the free PDF presentation
Modelling the air-liquid interface for lung-on-a-chip microfluidics
The next generation of lung models incorporates a semi-permeable membrane into microfluidic 3-dimensional organ-on-a-chip technology to more closely model the complex physiological lung microenvironment than traditional 2-dimensional cell culture.
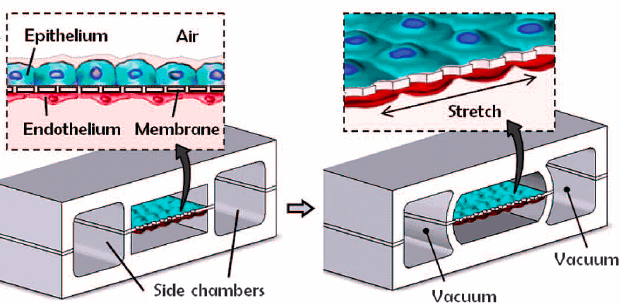
State-of-the-art lung-on-a-chip systems designed by Huh et al. at the Wyss Institute [1] contain two chambers, mimicking the air-filled alveolar sac and blood-filled capillary lumen, separated by a thin membrane representative of the air-blood barrier (Fig. 1).
The semi-permeable membrane was modeled using a flexible silicon-based organic polymer, polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS), and seeded with alveolar epithelial cells on the air interface and vascular endothelial cells on the plasma interface.
The introduction of cyclic strain via vacuum through dedicated microfluidic channels flanking the membrane was used to mimic the physiological stress faced by alveolar tissue with breathing, facilitating the replication of physiological interactions and functions. Specifically, junctions between adjacent cell types were formed, pulmonary surfactant was produced, and barrier porosity was close to physiological.
Features of a physiologically relevant air-liquid interface for microfluidic applications
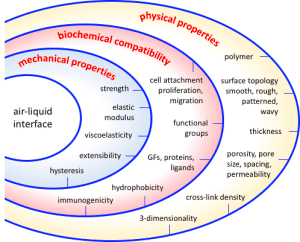
An essential feature of a model air-liquid interface is its ability to serve as a substrate for cell culture. Such substrates should promote cell attachment, proliferation, differentiation, and interactions and, ideally, enable replication of vital functional features of the tissue, such as gas permeability, surfactant production, and ciliary beating.
This review briefly outlines essential features of air-liquid interfaces and some current approaches to their design and modification to optimize lung-on-a-chip models. Specifically, we focus on the tunability of the air-liquid interface’s physical, biochemical, and mechanical properties. For more information, we refer the reader to a comprehensive review by Pasman et al. (2018) [2].
The air-liquid interface is commonly modeled using polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS). PDMS’s advantages are its low cost, easy and rapid casting ability, gas permeability, high optical transparency, and low autofluorescence. It is also flexible and relatively soft (elastic modulus ~1-3 MPa). PDMS can bind to other materials or itself after plasma oxidation treatment.
Disadvantages include its lack of biological and chemical cues for cells and high hydrophobicity. Depending on the application, PDMS membranes’ permeability, surface properties, and softness may benefit from being tuned.
Physical design considerations of the air-liquid interface in microfluidic devices
Physical properties such as membrane dimensionality, topography, porosity, and swelling affect cell behavior (e.g., adhesion and migration) and influence barrier function (i.e., permeability or leaking). Integrating higher control over various physical features will facilitate fine-tuning air-liquid interfaces and optimization for specific functions.
Pore architecture
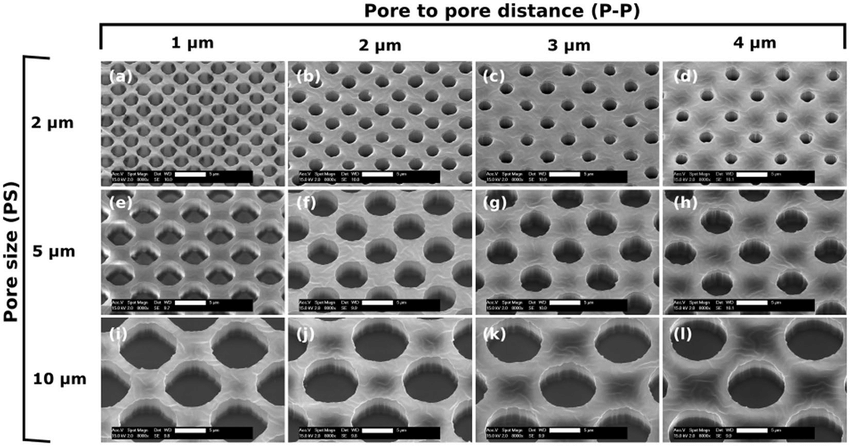
Porosity determines permeability to gas and nutrients and modulates the migration ability and interaction of cell types seeded on each membrane side [3]. Polycarbonate or polyethylene terephthalate (PET) membranes are two off-the-shelf choices commonly used to model the air-liquid interface and are available in various pore sizes.
Porous networks can be introduced to PDMS materials by particle leaching, gas foaming, or freeze-drying techniques. Alternatively, pore diameter, thickness, and pore-to-pore distance can be precisely customized using fabricated molds and masks (Fig. 3), and the pattern can be applied using various photolithography or etching techniques [3].
Topology
Physical (spatial) cues provided by surface topology modulate cell attachment, spreading, and alignment. Notably, the physiological microenvironment of cells is rarely a flat, smooth surface. Tuning the topology of the air-liquid interface can better mimic the convoluted texture of tissues, such as the large surface area and high curvature of the respiratory membrane.
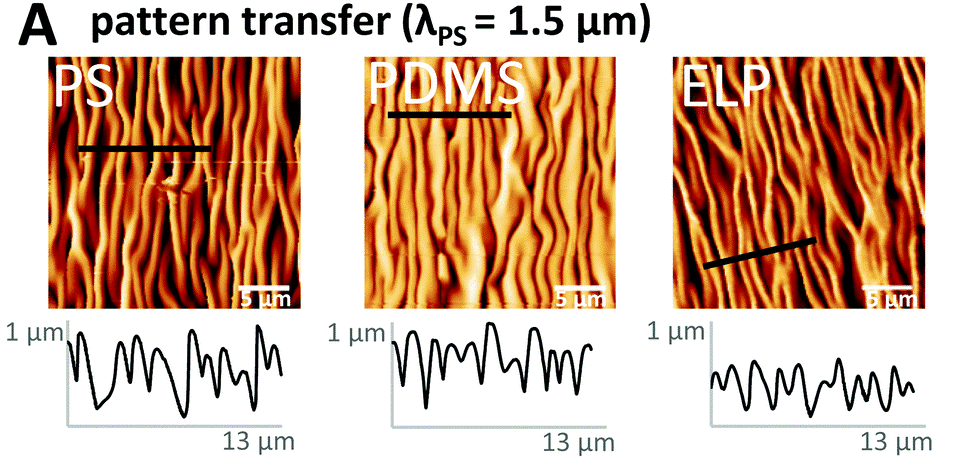
Material surfaces may be smooth, nano-roughened, or patterned with an array of grooves or custom designs, transferred by lithography or etching (Fig. 4) [4]. Tunable parameters include the spacing and height of micro-grooves, their relative orientation (parallel, semi-aligned, or random), and the angularity of edges (i.e., rectangular or rounded).
Dimensionality
The multi-layer geometry of native cell microenvironments can be modeled by increasing the dimensionality of scaffolds. Specifically, 3-dimensional scaffolds enhance the formation of cell-cell interfaces and tissue organization. Porous, fibrous networks that mimic native ECM scaffolds can be woven using electrospinning techniques (Fig. 5).
Fibre thickness material porosity and swelling can be controlled by modulating the flow rate [5]. Naturally, textured sacrificial casting substrates (e.g., sugar cubes) have been used to transfer complex 3-dimensional architectures to PDMS [6]. The degree of material swelling or contraction can be modified by the choice of polymer and cross-linker and the cross-linking density.

Bio-chemical design considerations of the air-liquid interface of microfluidic devices
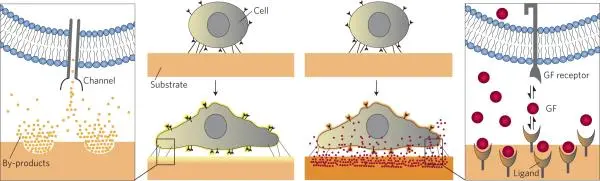
Biological and chemical stimuli such as growth factors, drugs, other cells, and cell adhesion molecules have long been recognized as essential regulators of cell behavior (Fig. 6) [7].
Modifying air-liquid interfaces to incorporate proteins and other bioactive compounds, tuning substrate wettability (hydrophobicity), or containing functional groups are some of the most commonly applied approaches to improving the growth and functionality of cells cultured at air-liquid interfaces.
In addition, substrates should be chosen such that degradation does not lead to cytotoxic by-products or adversely affect substrate porosity, topology, or mechanical properties.
Surface hydrophobicity
PDMS is a hydrophobic polymer. One disadvantage of the hydrophobic surface is that many small molecules and fluorescent drugs or dyes adsorb non-specifically. Plasma oxidation treatment renders the surface hydrophilic, but the effects are only temporary (hours).
Approaches to more permanently modify surface wettability include coating with poly-lysine, non-ionic surfactants, or adsorbing or immobilizing ligands, proteins, or functional groups (discussed below).
Matrix proteins
Cell biocompatibility of PDMS and other synthetic polymer substrates is commonly enhanced by treatment with extracellular matrix (ECM) proteins, mainly collagen and fibronectin [1], which promote and improve cell attachment and proliferation.
Proteins in solution may be adsorbed onto the surface of PDMS through coating or micro-contact printing or immobilized using a range of strategies such as treatment with (3-aminopropyl)triethoxy silane (APTES), cross-linkers (e.g., glutaraldehyde, PEG-based linkers) or plasma activation.
Functional groups
A wide range of functional groups (e.g., methacrylate, phosphate, carboxyl, amino, thiol, butyl groups) can be introduced to aid the adsorption and sequestration of biomolecules, such as glycoproteins and growth factors to enhance cell growth [7]. Functional groups can be added by grafting or polymerization methods, including surface plasma activation and chemical modification.
Mechanical design considerations of the air-liquid interface in microfluidic devices
In addition to biochemical and physical signals, it is increasingly evident that mechanical stresses are equally essential modulators of cell growth and tissue function (Fig. 7) [8].
For example, substrate stiffness can direct the lineage of stem cell differentiation [9], substrate stress-relaxation (a visco-elastic property) regulates cell spreading, proliferation [10] and scaffold remodeling [11], and mechanical stress applied during breathing influences the uptake of nanoparticles across the alveolar air-blood barrier [12].
Disease states such as emphysema, fibrotic tissue, and cancer present altered matrix stiffness compared to healthy tissue, influencing cell fate in disease progression, remodeling, and repair [13].
Microfluidic lung-on-a-chip cultures provide the means to model physiological fluid shear stress and dynamic forces of breathing. As such, mechanically tunable substrates are expected to enhance the functionality of these models.
Polymer blends
PDMS is comprised of long flexible monomer chains that are cross-linked at intervals. Once cured, this adaptable material is relatively soft (elastic modulus ~1-3 MPa) [14] and exhibits low viscoelastic hysteresis (energy dissipation) [15].
Varying the ratio of base to curing agent (e.g., 5:1, 10:1, 20:1) alters tensile stiffness and consequently modulates cell growth [16]. However, using a non-stoichiometric base-to-linker ratio may slow the release of uncross-linked monomers with undesirable effects.
An alternative approach has been to blend different PDMS types (e.g., Sylgard 184 and Sylgard 527) at optimal base-to-linker ratios, resulting in modulation of stiffness of over three orders of magnitude (elastic modulus spanning 5 kPa to 1.7 MPa) [17]. Several polymers commonly used as porous membranes (e.g., PC, PET, and PLA) are less suited to applications incorporating mechanical stimulation due to their high (GPa) stiffness [2].
ECM proteins
Fibrous extracellular matrix proteins respond to mechanical forces in tissues, including tensile strength (collagen), elastic extension, and recoil (elastin). Different tissues have different compositions of structural proteins and, hence, different mechanical properties, reflecting their physiological requirements.
Blending PDMS or other synthetic polymers with ECM proteins provides another strategy for modulating the mechanical properties of materials designed for air-liquid interfaces. Protein composition, cross-linker, and cross-linking density can be varied to tune mechanical properties [18].
The photos in this article come from the Elveflow® data bank, Wikipedia, or elsewhere if precised.
Review done thanks to the support of the MECH-LOC H2020-MSCA-IF-2017 – Marie-Curie Action:
“Individual Fellowships”
Grant agreement number: 793749
Written by Lisa Muiznieks, Postdoc
Contact:
Partnership[at]microfluidic.fr



References
- Huh, D., Matthews, B.A., Mammoto, A., Montoya-Zavala, M., Hsin, H.Y. and Ingber, D.E. (2010) Reconstituting organ-level lung functions on a chip. Science 328, 1662-1668
- Pasman, T., Grijpma, D., Stamatialis, D. and Poot, A. (2018) Flat and microstructured polymeric membranes in organs-on-chips. J. R. Soc. Interface 15, 20180351
- Quirós-Solano, W.F., Gaio, N., Stassen, O.M.J.A., Arik, Y.B., Silvestri, C., Van Engeland, N.C.A., Van der Meer, A., Passier, R., Sahlgren, C.M., Bouten, C.V.C., van den Berg, A., Dekker, R. and Sarro, P.M. (2018) Microfabricated tuneable and transferable porous PDMS membranes for organs-on-chips. Sci. Reports 8, 13524
- Paul, A., Stührenberg, M., Chen, S., Rhee, D., Lee, W.-K., Odom, T. W., Heilshorn, S.C. and Enejder, A. (2017) Micros- and nan-patterned elastin-like polypeptide hydrogels for stem cell culture. Soft Matter 3, 5665-5675
- Wise, S.G., Liu, H., Yeo, G.C., Michael, P.L., Chan, A.H.P., Ngo, A.K.Y., Bilek, M.M.M, Bao, S., and Weiss, A.S. (2016) Blended polyurethane and tropoelastin as a novel class of biologically interactive elastomer. Tissue Eng. Part A. 22, 524-533
- Bosi, S., Rauti, R., Laishram, J., Turco, A., Lonardoni, D., Nieus, T., Prato, M., Scaini, D. and Ballerini, L. (2015) From 2D to 3D: novel nanostructured scaffolds to investigate signalling in reconstructed neuronal networks. Sci. Reports 5, 9562-9572
- Murphy, W.L., McDevitt, T.C. and Engler, A.J. (2014) Materials as stem cell regulators. Nat. Materials 13, 547-557
- Engler, A.J., Sen, S., Sweeney, H.L., Discher, D.E. (2006) Matrix elasticity directs stem cell lineage specification. Cell 126, 677–689.
- Lv, H., Li, L., Sun, M., Zhang, Y., Chen, L., Rong, Y., Li, Y. (2015) Mechanism of regulation of stem cell differentiation by matrix stiffness. Stem Cell Res. & Ther. 6, 103-113
- Bauer, A., Gu, L., Kwee, B., Li, W.A., Dellacherie, M., Celiz, A.D., Mooney, D.J. Hydrogel substrate stress-relaxation regulates the spreading and proliferation of mouse myoblasts. (2017) Acta Biomater. 62, 82-90
- Darnell, M., Young, S., Gu, L., Shah, N., Lippens, E., Weaver, J., Duda, G., Mooney, D. substrate stress-relaxation regulates scaffold remodeling and bone formation in vivo. (2017) Adv. Healthcare Mater. 6, 1601185
- Schürch, D., Vanhecke, D., Clift, M.J.D., Raemy, D., de Aberasturi, D.J., Parak, W.J., Gehr, P., Petri-Fink, A. and Rothen-Rutishauser, B. (2014) Modeling nanoparticle-alveolar epithelial cell interactions under breathing conditions using captive bubble surfactometry. Langmuir 30, 4924-4932
- Hinz, B. (2012) Mechanical aspects of lung fibrosis. Proc. Am. Thorac. Soc. 9, 137-147
- Johnston, I. D., McCluskey, D. K., Tan, C. K. L. and Tracey, M. C. (2014) Mechanical characterization of bulk Sylgard 184 for microfluidics and microengineering. J. Micromech. Microeng. 24, 035017
- Deguchi, S., Hotta, J., Yokoyama, S. and Matsui, T.S. (2015) Viscoelastic and optical properties of four different PDMS polymers. J. Micromech. Microeng. 25, 097002
- Park, J. Y., Yoo, S. J., Lee, E.-J., Lee, D. H., Kim, J. Y. and Lee, S.-H. (2010) Increased poly(dimethylsiloxane) stiffness improves viability and morphology of mouse fibroblast cells
- Palchenko et al. (2012) PLoS One
- Yeo, G.C., Aghaei-Ghareh-Bolagh, B., Brackenreg, E.P., Hiob, M.A., Lee, P. and Weiss, A.S. (2015) Fabricated elastin. Adv. Healthcare Mater., 4, 2530–2556
Check the other Reviews
FAQ - Air-liquid interface and optimized cell culture substrate for a microfluidic lung-on-a-chip application
1) What is the air-liquid interface in the physiology of the lungs?
Lung exchange occurs at the air-liquid interface, which is a thin layer between gas exchange between air in alveolar sacs and blood in capillaries. This interface comprises of alveolar epithelial cells that have a common basement membrane with vascular endothelial cells. A phospholipid known as pulmonary surfactant lines the interface decreasing surface tension and increasing barrier functionality. Breathing of air above this interface is done at a rhythmic rate by the beating of cilia to expel mucus and particles up the airway.
2) What are the ways in which lung-on-chip systems recap air-liquid interface?
The current system of lung-on-chip incorporating two chamber microfluidic devices with a semi-permeable barrier that simulates air-blood barrier. One of the sides of the alveolar epithelial cells are incubated with air, and the other with the presence of vascular endothelial cells that are incubated with culture medium that mimics blood presence. The first design proposed by Huh and coworkers to the Wyss Institute consists of microfluidic channels in which the membrane is subjected to cyclic vacuum, which is an imitation of breathing movements and physiological mechanical stress.
3) What are the reasons why PDMS is a popular choice of air-liquid interface membrane?
The most prevalent material is polydimethylsiloxane due to its numerous benefits such as low cost, easy/rapid transformation, high oxygen and carbon dioxide exchange rate via gas permeability, high optical transparency to be viewed under a microscope, low autofluorescence to be imaged, and most suitable flexibility with elastic modulus of around 1-3 MPa. PDMS has the capability of bonding and bonding with other materials when it is subjected to plasma oxidation which helps it absorb devices.
4) What are the key drawbacks of PDMS membranes?
PDMS is limited in a number of aspects such as being highly hydrophobic leading to unspecific adsorption of drugs and fluorescent molecules, inability to adsorb inherent biological and chemical cues to allow cell growth and attachment, and surface hydrophilicity that is short lived, only several hours after plasma treatment. Moreover, PDMS membranes can take further tuning of permeability, surface properties, mechanical stiffness on top of their native properties depending on their application.
5) Control of membrane porosity: Why and how?
Porosity defines the permeability of membranes to gases and nutrients and regulates the migration and communication of cell types on the opposite sides. Leaching of particles, foaming of gases or freeze-drying can be used to introduce porous networks. Alternatively, the diameter and thickness of pores, and the thickness between pores can be strictly tailored using fabricated masks and molds via photolithography or etching. Alternatives to PDMS are also in the form of off-the-shelf polycarbonate or PET membranes of various pore sizes.
6) How are cell cultures enhanced on air-liquid interfaces?
Cell biocompatibility is improved in several ways such as it is coated with extracellular matrix proteins like collagen and fibronectin to stimulate attachment and growth, alteration of the surface hydrophobicity using poly-lysine or surfactants and addition of functional groups, such as methacrylate, amino, or thiol group. Such changes may be done using adsorption, micro-contact printing, chemical cross-linkers or using plasma activation methods. These treatments aid in the cell connection, proliferation, and retention of specialization.
7) What is the impact of the surface topography on cell behavior in lung-on-chip?
Topographical features on the surface give mechanical information to regulate cell adhesion, dispensation, and orientation. The physiological lung setting is not flat but has a convoluted texture and a high surface area and curvature. Both nano-roughness on surfaces and micro-grooves of different spacing, height, and orientation can be engineered. Electrospinning fibrous scaffolds can be three-dimensional, permitting the natural architecture of the extra-cellular matrix to be recapitulated, generating better cell-cell interfaces and tissue organization than is possible on a flat surface.
8) What are the importance of mechanical properties to lung-on-chip models?
The mechanical properties have a serious effect on cell fate and tissue functionality. Mechanical stiffness of substrates can guide stem cell differentiation, cell spreading and proliferation can be regulated by mechanical stress relaxation, mechanical stress at the air-blood interface can influence the uptake of nanoparticles across the air-blood barrier. Such disease conditions as emphysema, fibrosis and cancer have a different matrix stiffness than healthy tissue. Mechanically tuneable substrates with cyclic strain enhance physiological relevance in models by activating surfactant synthesis, creating correct cell junctions, and getting barrier porosity within the range of native values.
9) What can be done to tune substrate stiffness in PDMS membranes?
Stiffness may be adjusted using the proportion of PDMS base to curing agent but non-stoichiometric ratios can emit uncross-linked monomers deleteriously. A superior model entails combination of various types of PDMS at the most appropriate proportions and creates stiffness modulation in three orders of magnitude between 5 kPa and 1.7 Mpa. Alternatively, mechanical properties can be tuned by mixing PDMS with biological cues such as collagen or elastin, and control of mechanical properties can be done by varying protein mixture, cross-linker type, and cross-linking density.
10) Which physiologically-relevant lung-on-chip models are physiologically validated by their functional outcomes?
Principles of validation markers comprise the establishment of tight junction between neighboring epithelial and endothelial cells, pulmonary surfactant is produced under mechanical force by alveolar cells, the barrier permeability is physiologically comparable, ciliary beating is required to clear particles and responses to mechanical stimulation. Elaborated models exhibit superior uptake and transport investigations of drugs and nanoparticles, conditions modeling such as fibrosis, and the governing capacity to retain differentiated cell phenotype and functionality over prolonged culture periods than conventional systems.

