Microfluidics for biology research
Author
Guilhem Velvé Casquillas
Publication Date
October 13, 2015
Keywords
microfluidic revolution
biology research
Organ-on-a-chip
cell culture
Droplet Microfluidics

Need advice for your biology research?
Your microfluidic SME partner for Horizon Europe
We take care of microfluidic engineering, work on valorization and optimize the proposal with you
You work in biology research and wonder how microfluidics can help you? Let’s discover together how microfluidics can benefit your research!
The microfluidic revolution: we take care of microfluidics, you focus on biology research!
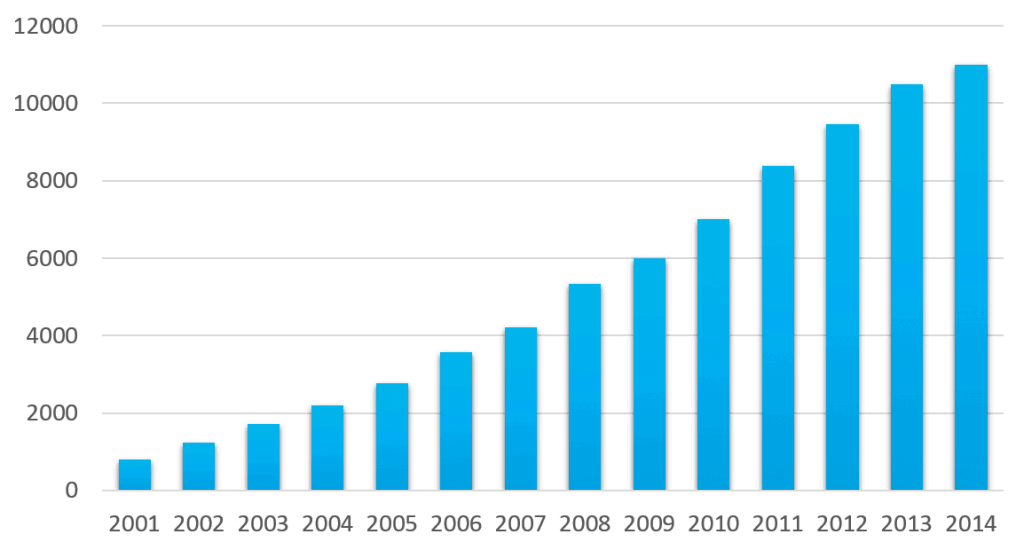
10X more publications on microfluidics and biology research since 2002
A little bit of history: What is microfluidics?
Microfluidics emerged at the beginning of the 1980s and took advantage of microfabrication technologies used for transistors and microprocessors to handle small amounts of liquids inside micrometer to nanometer scale channels.
In the 2000s, technologies based on molding micro-channels in polymers such as PDMS (PolyDiMethilSiloxane) enabled fast development of microfluidics by allowing rapid prototyping in any research lab.
Today, microfluidics is a mature technology that provides efficient tools for multiple research areas, specifically biology research.
How microfluidics can enhance cell biology research?
Microfluidic systems are compatible with microscopy and conventional biology assays.
Applications: Cell culture, live cell imaging, 3D cell culture…
Its micrometer scale is the same as cells’ scale, enabling a fast medium switch.
Applications: Single-cell analysis, calcium imaging, drug response studies…
Microfluidics enable the finest flow control and stable concentration gradients.
Applications: Chemotaxis, shear stress assays, hydrodynamic cell trapping…
Microfluidics easily allows parallelization and thus promotes high throughput screening.
Applications: Drug screening, quantitative cell biology, bioinformatics…
Work with the world leader in microfluidic instrumentation
How can we help you to add microfluidics in your biology research?
Define your experiment
Our team of PhDs are available to discuss your project, understand your goals and assess your needs.
A setup fitted to your needs
Together, we will define the best setup according to both your experimental needs and your budget.
Setup installation in your lab
Our systems are plug & play and our team is available should you require assistance. We can install the setup in your lab and perform trial experiments with you.
Experiment with ease of mind
Our support team always answers within 24 hours if you have any questions about microfluidics and biology research.
Check more Quick Tips
FAQ - Microfluidics for biology research
- What is microfluidics and when did it emerge as a research field?
Microfluidics emerged in the early 1980s as a technology that leverages microfabrication techniques originally developed for transistors and microprocessors to manipulate small volumes of liquids within channels at the micrometer-to-nanometer scale. In the 2000s, polymer-based technologies, particularly using PDMS (polydimethylsiloxane) molding, enabled rapid prototyping capabilities in any research laboratory, democratizing access to microfluidic tools. Today, microfluidics is a mature technology that provides efficient solutions across multiple research domains, particularly in the biological sciences.
- How has microfluidics adoption in biology research evolved over the past two decades?
Scientific publications combining microfluidics and biology have increased tenfold since 2002, demonstrating the technology’s growing integration into biological research workflows. This exponential growth reflects both technological maturation and wider recognition of microfluidics’ unique capabilities for addressing biological questions. The technology has transitioned from specialized early-stage development in engineering laboratories to mainstream adoption across diverse biological research areas, including cell culture, single-cell analysis, organ-on-chip platforms, and high-throughput screening applications.
- What are the key advantages of microfluidics for cell biology research?
Microfluidic systems offer several critical advantages. First, they are fully compatible with conventional microscopy and standard biology assays, facilitating integration into existing workflows. Second, the micrometer-scale resolution matches cellular dimensions, enabling rapid medium switching, essential for single-cell analysis, calcium imaging, and drug response studies. Third, microfluidics provides precise flow control and stable concentration gradients, crucial for chemotaxis studies, shear stress assays, and hydrodynamic cell trapping. Finally, the technology readily supports parallelization, promoting high-throughput applications in drug screening, quantitative cell biology, and bioinformatics.
- What types of biological applications can microfluidics support?
Microfluidics supports a wide range of biological applications: cell culture and live-cell imaging, 3D culture systems, single-cell analysis, calcium imaging, drug response testing and screening, chemotaxis studies, shear stress assays, hydrodynamic cell trapping, and high-throughput screening platforms.
Microfluidic systems are able to precisely control the cellular microenvironment, including flow, gradients, and mechanical forces, while remaining compatible with standard analytical and imaging techniques. As a result, microfluidics is well-suited to investigations at the molecular, cellular, and tissue scales.
- How does the Microfluidics Innovation Center support researchers adopting microfluidics?
The MIC provides comprehensive support through a structured four-stage process. First, our team of engineers and PhDs discusses projects to understand goals and assess needs. Second, we collaboratively define optimal setups that balance experimental requirements with budget constraints. Third, we offer plug-and-play systems with installation support, including setup in user laboratories and trial experiments. Fourth, we provide support with guaranteed responses to any questions regarding microfluidics and biological research, ensuring researchers can focus on their biological investigations while we manage technical microfluidic aspects.

