On-demand peptide synthesis for personalized medicine: ElectroMed
Author
Christa Ivanova, PhD
Publication Date
January 14, 2020
Status
Keywords
personalised medicine
Lab-on-a-chip
microfluidic multiplexing
ligand-receptor interactions
proteomics
electrochemically‑directed peptide synthesis
Your microfluidic SME partner for Horizon Europe
We take care of microfluidic engineering, work on valorization and optimize the proposal with you
Microfluidics is a technology of choice for personalized medicine. In the ElectroMed project, complex fluid handling in microfluidic devices will synthesize patient-specific peptides on demand.
Microfluidic complex fluid handling system for personalized medicine: introduction
The ElectroMed project was honored to be presented as one of the “Breakthrough ideas” in the first European Innovation Council (EIC) newsletter in Spring 2020.
This newsletter was explicitly dedicated to COVID-19, and the partners in ElectroMed expressed their commitment to contribute to possible diagnosis solutions and vaccine developments to overcome the crisis.
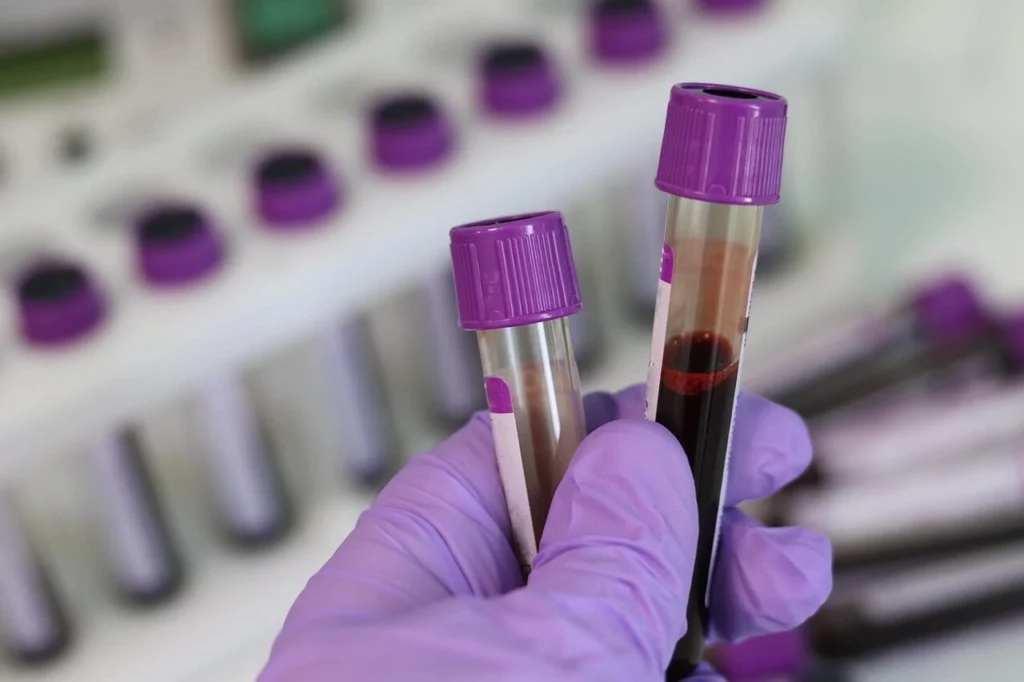
Proteomics is increasingly used as a diagnostic tool and therapeutic solution for personalized medicine. The customized screening of proteins is currently performed thanks to immunosensors, using specific ligands to capture and detect proteins.
However, no tool is available for fast, accurate, cost-effective protein screening at the patient’s level. To achieve that, a system able to program the synthesis of the personalized choice of ligands and to control the ligand-receptor assembly to ensure the best sensing performance and reliable detection is needed.
On-demand peptide synthesis for personalized medicine: project description
ElectroMed will propose a user-friendly platform to program electrochemically-directed peptide synthesis thanks to a microfluidic multiplexing system controlled by a software to boost the use of proteomics in personalized medicine. The ligand-receptor complexes will then be detected and quantified thanks to label-free sensors based on nanomaterials.
In this project, we will propose an effective solution for the complex fluid handling of up to 24 solutions (amino acids, solvents, and samples) in the microfluidic device. The system will enable an automated injection of the different reagents needed for the ligand synthesis, that is to say, for the personalized and controlled synthesis of peptides.
A combination of Elveflow pressure controller and flow switch matrices will be used to achieve this complex fluid handling under the control of our dedicated software. The ElectroMed project aims to develop and validate a proof-of-concept prototype that will make using proteomics for personalized medicine possible.
The developed prototype could also greatly interest the food sector (allergens, GMOs, or toxin detection) and the environmental or defense sector.
As of spring 2021, a proof of concept for the peptide synthesis has been developed at Elvesys, enabling the sequential injection of 9 different solutions, the activation of amino acids by mixing, and the rinsing of the microfluidic line to avoid cross-contamination.
The next step will be to integrate the sensors developed by our collaborators into the microfluidic line to perform peptide coupling and biomolecule recognition into the microfluidic line.
Results from this project
In the light of the Electromed project, we have developed an automated fluidic control pack for spatial transcriptomics.
Funding
This project has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 FETOPEN under grant agreement No 862539 (ElectroMed).

Check our Projects
FAQ – On-demand peptide synthesis for personalized medicine: ElectroMed
What is actually the problem that ElectroMed is solving?
There is a bottleneck of dirty matrices (plasma, CSF, saliva) and small volumes in clinical peptidomics. ElectroMed addresses both: microfluidics control that and tames complicated fluids, and on-chip electrochemistry which selectively captures, cleans and releases peptides to be further analyzed.
What is the practical application of the term electrochemically-enabled peptidomics?
Under the applied potential, the peptides are concentrated onto micro-electrodes, diverted or flushed are salts, macromolecules and lipids. A regulated polarity/ buffer switch will subsequently release the enriched fraction of peptides. Imagine that it is solid-phase extraction without the dead volumes and with milliseconds control.
What is the need for microfluidics in this case, but not just better bench chemistry?
At the microliter level, diffusion times are not long, and interfaces are stable. That allows us to create tight gradients, maintain low shear, and direct fractions without cross-contamination. Practically speaking: reduced background, reduced carryover artifacts, and sample-in/clean-peptide-out procedures that accommodate rare or valuable specimens.
What is the scaling of the system -throughput and multiplexing?
Chips are arrayed. One device can process several lanes simultaneously, it is a realistic starting envelope of 8-24 samples per day per instrument, however, it is variable based on the complexity of the matrices and the level of QC required. In the targeted panel case, it is possible to use capture electrodes zoned to allow sequential elutions (matrix clean-up – broad capture – target-biased release).
What is your metric of validation that you use during a run?
Back-pressure, presence of transient currents determined, conductivity dropped across desalting zones and a pre/post-enrichment ratio of peptides were restored using stable isotope standards. Batches are taken in cases of recovery, CV and carryover as per pre-determined predetermined levels. False reactions cause automatic rinse/pulse or rate of flow reactions.
What would be the process of collaboration with MIC in Horizon Europe?
MIC normally spearheads microfluidic architecture, the electrochemical integration of modules, assay automation, and exploitation design. Coupled with a successful SME, incorporating a performing SME makes a consortium robust: in several European projects, the inclusion of MIC on board has approximately doubled the chances of success regarding the official baseline rates. We also provide early prototypes and anchor milestones – reviewers are responsive to risk reduction.